Table of Content
Blog Summary:
In this blog, we will guide you through the migration process of your Laravel database using the php artisan migrate command. This powerful tool ensures that your database schema stays in sync with your application’s changes, making database management more efficient and streamlined. Using PHP Artisan Migrate, you can easily apply all pending migrations to ensure a smooth update process.
Table of Content
If you are building web applications with Laravel, keeping your database schema aligned with your codebase is crucial. That is where the built-in migration command, PHP artisan migrate, comes in handy, a simple yet powerful CLI tool that runs pending migrations. Hence, your production database reflects your latest models and changes. Based on a survey conducted by BuiltWith, there are 2,579,903 websites built with Laravel; out of these, 1,130,062 are live, highlighting its strong and active user base.
In this piece, we will walk through a step-by-step process to help you seamlessly migrate your Laravel database, discuss the key benefits of using PHP’s artisan migrate, and share real-world use cases.
In Laravel development, the php artisan migrate command is essential for executing database migrations. Migrations are like version control for your database schema, allowing developers to define new tables and relationships in PHP code. This command simplifies managing database changes across different environments.
When you run a php artisan schema, Laravel checks for any pending migrations and applies them in sequence. It automatically creates database tables and indexed columns from the migration files. This ensures consistency between the local, staging, and production environments.
Additionally, Laravel offers related commands, such as php artisan migrate: rollback to undo the last batch of migrations and php artisan migrate: refresh to reset and reapply all migrations. These commands are incredibly useful during development, ensuring your database stays up to date without manual intervention.
By using php artisan migrate, Laravel developers can focus on building features while maintaining a clean and version-controlled database structure.
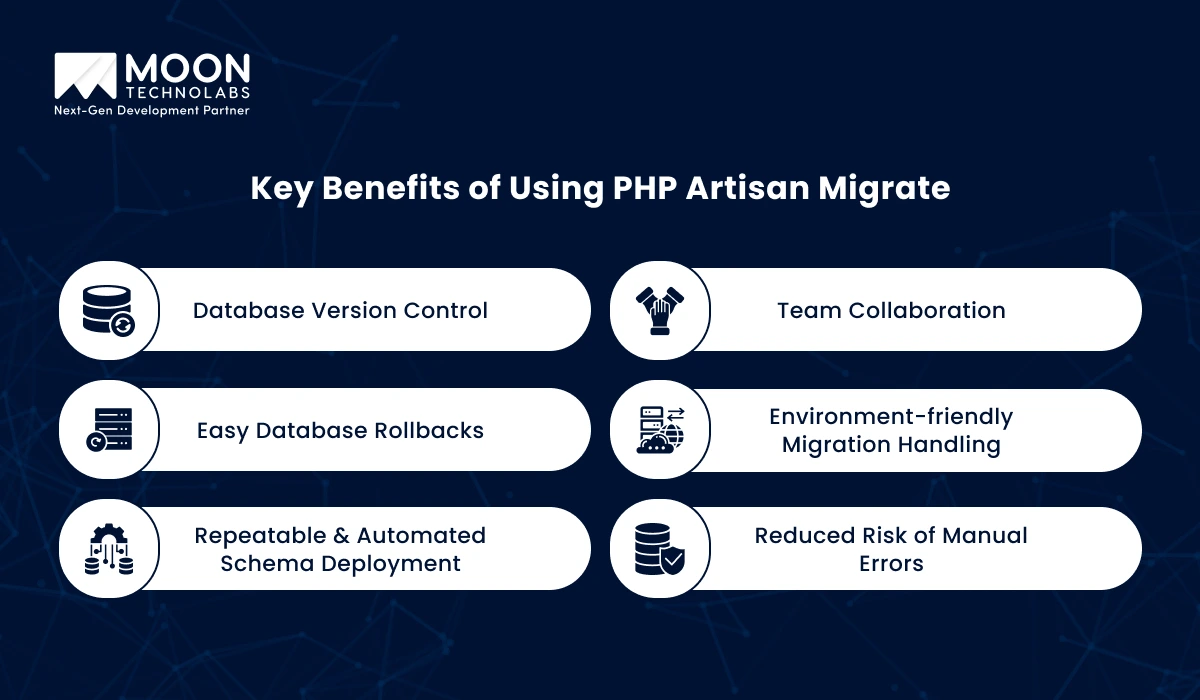
Have a look at some of the key benefits of using PHP Artisan Migrate for efficient database management and version control.
The Migrate Artisan command helps track and version database changes, ensuring consistency across different environments. It allows developers to share and synchronize schema updates easily.
Migrations simplify team collaboration by enabling developers to share migration files, ensuring everyone uses the same database structure without manual syncing.
Mistakes happen, but with PHP Artisan Migrate, rolling back migrations is simple. You can easily undo changes and restore the database schema to a previous state.
Migrations can be environment-specific, making it easier to apply the right changes in local, staging, or production environments, avoiding conflicts or data loss.
Automate and repeat database schema deployments with ease. Migrations ensure that updates are consistently applied across all environments without manual intervention.
By using migration files to define schema changes programmatically, PHP Artisan Migrate reduces the risk of manual errors and ensures more stable database management.
You Might Also Like:
Top Benefits of Laravel that You Get with No Other PHP Framework!
In Laravel, migrations provide a structured way to manage database schema changes over time. Migrations allow you to create and modify database tables and columns in a consistent, version-controlled manner, helping your team work with databases without manually writing complex SQL.
There are several types of migration operations you can perform in Laravel:
Running migrations in Laravel applies any outstanding migrations to the database. This operation ensures you manage the database schema and verify that it is up to date with the migration files in your project.
Command:
php artisan migrate
This will apply to all migrations that haven’t been run yet. The migrate command checks the migration table (which Laravel automatically creates) and runs any migrations that haven’t been marked as “run.”
Rolling back a migration means reverting the most recent batch of migrations applied. This operation is useful when you want to undo recent changes made to your database schema.
Command:
php artisan migrate:rollback
By default, this will roll back the last batch of migrations. If you want to roll back multiple batches, you can specify the –step option.
php artisan migrate:rollback --step=2
This command will roll back the last two migration batches.
An effective reset migration removes all migrations from the database and reverts all schema changes. This is useful when you want to undo all migrations and start fresh, completely.
Command:
php artisan migrate:reset
This command rolls back all migrations in reverse application order, restoring the database to its original state before any migrations were run.
Refreshing migrations combines rolling back and re-running all migrations. This is useful when you want to reset the database schema and reapply all migrations without manually rolling back each migration. It can be particularly helpful during development to quickly test changes in your migration files.
Command:
php artisan migrate:refresh
By default, this command rolls back all migrations and then re-runs them. You can also use the –seed option to run database seeders after refreshing the migrations, which will populate your database with test data.
php artisan migrate:refresh --seed
This command is often used during development to reset the database and start with fresh data.
Laravel provides built-in seeding functionality to populate your database with test data. Seeding is often used alongside migrations to populate the database with default or mock data after a migration has run.
You can seed your database manually using the db:seed Artisan command:
Command:
php artisan db:seed
This will run the DatabaseSeeder class located in the database/seeders directory. Inside this class, you can define seeders for each of your models.
If you want to run the seeder automatically after running migrations, you can use the –seed option with the migrate:refresh command:
php artisan migrate:refresh --seed
This will first rollback and then reapply all migrations, followed by seeding the database with data defined in the seeder classes.
This command runs all pending migrations (not yet executed).
Use when:
Rolls back the last batch of migrations. A batch is a group of migrations run together.
Use when:
Rolls back all migrations, essentially undoing every migration that has been executed.
Use when:
Resets all migrations and then runs migrate again.
Equivalent to:
php artisan migrate:reset
php artisan migrateUse when:
Drops all users table and runs all migrations from the start.
Difference from refresh:
Use when:
Forces the migration to run in production mode.
Use when:
Runs migrations from a specific directory or file path.
php artisan migrate --path=database/migrations/custom
Use when:
Runs migrations and then triggers the DatabaseSeeder.
Equivalent to:
php artisan migrate
php artisan db:seed
Use when:
Before you begin, ensure that Laravel is properly installed on your system. You can verify this by running the following command in your terminal:
php artisan --version
If you see the Laravel version printed out, you’re all set.
To make sure your application can connect to your database, configure your .env file with the correct database connection details. Open the .env file in the root of your Laravel project and set the database parameters as follows:
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=your_database_name
DB_USERNAME=your_database_user
DB_PASSWORD=your_database_password
After updating the .env file, run the following command to clear the configuration cache:
php artisan config:clear
To create a new migration file, you can use the Artisan make:migration command. This command will generate a new file where you can define your schema changes.
Here’s how you can create a migration for a table:
php artisan make:migration create_users_table
This will generate a file in the database/migrations directory with a name like create_users_table.php. The timestamp in the file name ensures that migrations are run in the correct order.
Inside your migration file, you’ll define the structure of your new database table. This is done inside the up() method. You can use Laravel’s Schema Builder to define columns for the table.
Example of defining a users table with name, email, and password columns:
public function up()
{
Schema::create('users', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id(); // auto-incrementing primary key
$table->string('name');
$table->string('email')->unique();
$table->timestamp('email_verified_at')->nullable();
$table->string('password');
$table->rememberToken();
$table->timestamps();
});
}
In the above given example:
Once your migration file is ready, you can apply the migration to your database by running the following Artisan command:
php artisan migrate
This command will run all pending migrations that have not been applied yet, creating or modifying tables in your database as specified in the migration files.
After running the migration, you can check your database to confirm that the table has been created.
If you need to undo a migration, you can use the migrate:rollback command. This will roll back the last batch of migrations that were run.
To rollback the last migration:
php artisan migrate:rollback
To rollback all migrations (i.e., revert everything back to the initial state), use:
php artisan migrate:reset
If you need to refresh the database (rollback and re-run all migrations), use:
php artisan migrate:refresh
Once you’ve run your Laravel database migration, you should test your database schema to ensure that everything has been created correctly.
$users = DB::table('users')->get();
dd($users);
When deploying migrations to production, exercise caution as migrations can affect critical data. Here are key tips for the safe deployment process:
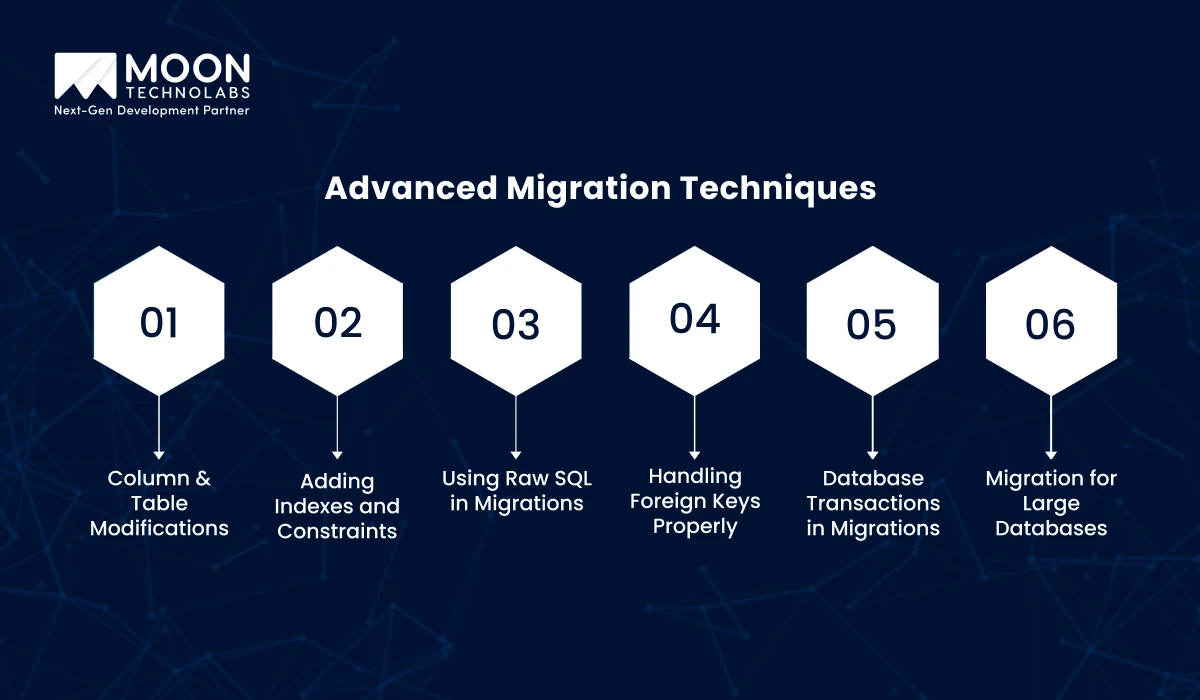
Modifying columns and tables is common in database evolution, but requires careful planning to avoid data loss or downtime, especially when changing column types or adding non-nullable columns.
Indexes optimize query performance, while constraints (e.g., unique, foreign key) maintain data integrity. Both must be carefully managed to balance performance and consistency.
Raw SQL enables complex operations that an ORM cannot, giving greater control over schema changes, data transformations, and performance optimizations.
Foreign keys ensure referential integrity between tables. It’s vital to define cascading actions (e.g., ON DELETE CASCADE) and handle foreign key violations carefully to maintain data consistency.
Transactions bundle multiple changes into a single atomic operation, ensuring either all changes succeed or none, preserving database consistency during schema changes.
For large datasets, breaking operations into smaller chunks minimizes locking and reduces the risk of timeouts, enabling efficient and scalable migrations.
When running Laravel database migrations with php artisan migrate in Laravel, developers often encounter various errors. Below are some of the most common errors encountered during migrations, along with tips for troubleshooting and resolving them.
An invalid SQL syntax error can occur if there is a mistake in the migration script, particularly in the structure of SQL commands that Laravel tries to generate.
How to Fix:
Foreign key constraints are often violated during migrations if the referenced column or table does not exist, or if the data types of the related columns do not match.
How to Fix:
This error occurs when Laravel can’t find the migration file, either because it’s missing or incorrectly named.
How to Fix:
Laravel tracks the migrations that have been run in a special table called migrations. If this table is missing or corrupted, migrations will fail.
How to Fix:
This error occurs when a migration attempts to add a column or table that already exists in the database, often due to previous migrations or incomplete rollback.
How to Fix:
Permission errors typically occur when the database user lacks sufficient privileges to perform the migration actions. Similarly, environment errors can occur when configuration settings are mismatched.
How to Fix:
PHP Artisan Migrate is a powerful tool in Laravel for managing and evolving database schemas. Here are some key use cases where it simplifies database management:
As apps grow, database structures need regular updates. Laravel Artisan Migrate automates schema changes, ensuring consistency across environments. Developers can easily apply migrations by running “php artisan migrate,” ensuring a seamless, error-free update process, especially as the application scales.
For high-traffic apps, downtime is costly. Artisan Migrate enables zero-downtime schema updates by allowing changes such as adding columns without interrupting services. Laravel’s transactions ensure database integrity during migrations.
In large teams, managing migrations can be tricky. With Artisan Migrate, developers can create and apply migrations independently, keeping the database schema consistent across all environments. Rollbacks are easy, enabling quick fixes if issues arise.
In multi-environment setups (e.g., development, staging, production), Artisan Migrate ensures migrations are applied consistently across all environments. For example, running “php artisan migrate –env=production” ensures that production databases are always up to date without affecting other environments.
In agile workflows, the database needs to evolve quickly. Artisan Migrate supports rapid iteration by allowing migrations to be created, applied, and rolled back with ease. This ensures the database evolves alongside the application without disruptions.
Moon Technolabs is a top choice for Laravel and migration development, offering expert solutions tailored to meet specific business needs. Their skilled team delivers scalable, high-performance web applications using the latest Laravel features, ensuring a seamless user experience. With a focus on quality and client satisfaction, they guarantee robust, customized solutions for every project.
In addition to Laravel development, we specialize in smooth migrations, helping businesses transition from legacy systems to modern platforms with minimal downtime. Their proven expertise ensures secure, efficient data migration while maintaining operational continuity, making them a reliable partner for seamless digital transformations.
Quickly migrate your Laravel database with simple Artisan commands for a smoother and more efficient development process.
Migrating your Laravel database using PHP Artisan is an essential skill for maintaining a smooth, efficient workflow in your development process. With its simple commands, Artisan makes database changes, rollbacks, and version control effortless, ensuring consistency across various environments. So, whether you’re managing a small project or working on a large-scale application, this tool helps you avoid errors and reduce manual effort, saving you time and resources.
If you’re looking to elevate your project and ensure everything is handled expertly, hire PHP developers from Moon Technolabs and bring a wealth of knowledge to optimize your migrations, streamline workflows, and help you focus on building the best version of your application.
01
02
03
04
05
Submitting the form below will ensure a prompt response from us.