Table of Content
Blog Summary:
Is your healthcare app really secure? With 90% of medical apps missing key protections, security testing isn’t optional — it’s critical. This ultimate QA checklist uncovers real-world risks and proven strategies to keep your app safe, compliant, and patient-ready.
Table of Content
Healthcare application and domain testing are essential for ensuring the quality, security, and compliance of healthcare software across all devices and platforms. From telehealth platforms to medical device companions and electronic health records, how can QA strategies effectively cover them all?
Our QA milestone approach provides a clear, structured path that reinforces functional testing while boosting both process efficiency and overall effectiveness. These rigorous processes help address the unique challenges of the healthcare industry, including regulatory requirements and interoperability, to ensure the delivery of effective healthcare solutions.
Such a cohesive journey, where each milestone builds upon the last, helps drive faster, safer, and more reliable healthcare app releases.
In this blog, we aim to solve such daily challenges and explore various test scenarios that founders, QA leads, project managers, IT managers, and compliance officers face when ensuring mobile healthcare apps are secure and reliable through an effective testing strategy.
While healthcare apps have transformed the delivery and reception of healthcare to millions of people, the healthcare industry faces significant challenges related to cybersecurity threats.
Common hurdles such as detecting security loopholes, validating encrypted data transmissions, and simulating real-world user scenarios are integral to the QA routine. Compliance testing is essential to ensure that healthcare applications adhere to healthcare regulations such as HIPAA and local laws, safeguarding legal compliance and enforcing data security.
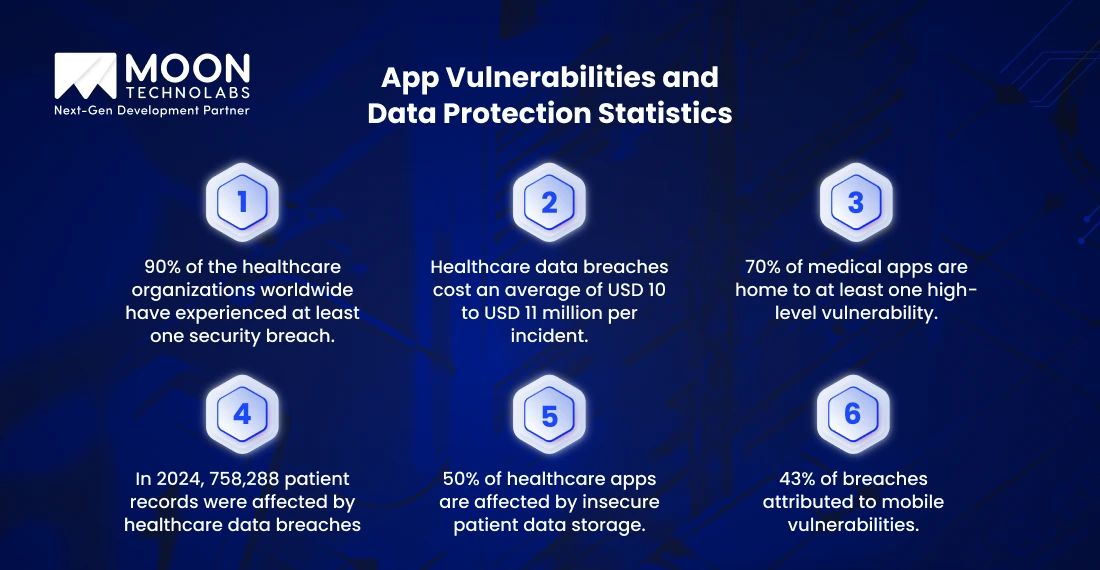
According to Astra, 90% of the healthcare organizations worldwide have experienced at least one security breach. Out of these, 30% are large hospitals that account for some of the major breaches. The impact of these breaches on the financial landscape is equally devastating, highlighting the importance of managing testing costs effectively.
IBM suggests that today, healthcare data breaches cost an average of USD 10 to USD 11 million per incident. Since health applications present a particularly vulnerable front, 43% of the data breaches are attributed directly to mobile app vulnerabilities.
On top of that, according to the National Institutes of Health, 70% of medical apps are home to at least one high-level vulnerability related to data security, emphasizing the need for automated testing to identify and mitigate these risks.
A study by Intellect Health Market indicates that by the end of 2025, the global digital health market is set to surpass USD 660 million. Patient records, including sensitive patient information, are compromised every single day. In 2024, at least 276,775,457 individuals were affected by healthcare data breaches.
The 758,288 patient records have been affected due to the vulnerable frontier that they have. Protecting sensitive patient information is crucial not only for privacy but also for maintaining health insurance portability, ensuring that patients can securely transfer their health and insurance data even after a breach, which can be supported through automated testing.
All of this underscores the importance of healthcare app QA, which incorporates various types of testing, as a critical pillar in delivering safe and trustworthy digital health solutions.
Healthcare mobile apps face unique security challenges that transform common vulnerabilities into life-threatening risks. Rigorous testing of healthcare applications and healthcare software is essential for identifying and mitigating security threats, ensuring regulatory compliance, maintaining the integrity of sensitive patient data, and understanding various types of testing.
The OWASP Mobile Security Project has identified the most critical threats that healthcare software testing must address:
Ongoing testing of healthcare is necessary to ensure continuous testing and protection against emerging threats, as well as to maintain the highest standards of software quality and security.
What happens when a cardiac monitoring app stores heart rhythm data in plaintext on the device? When a patient’s phone is stolen, thieves get access to personal information as well as insights into when the patient is most vulnerable to cardiac events.
In addition to security risks, maintaining data accuracy is crucial to ensure that software requirements are met, enabling a robust testing strategy that supports reliable clinical decision-making and protects patient safety.
Security researchers testing healthcare APIs found that every single endpoint they examined contained broken object-level authorization (BOLA) vulnerabilities. This means unauthorized users could potentially access any patient’s complete medical history. Hence, it’s a critical area for our dedicated testing team to focus on, simply by changing a number in a web request.
To uncover and address authentication and authorization issues, it is essential to employ various software testing types, including security, interoperability, and usability testing, during the development of healthcare software.
A telemedicine app transmitting patient consultations over unencrypted channels is essentially broadcasting private medical conversations to anyone with basic network monitoring tools.
Secure protocols are essential not only for protecting sensitive information but also for ensuring smooth data exchange between healthcare systems, devices, and healthcare providers, which is crucial for efficient test execution.
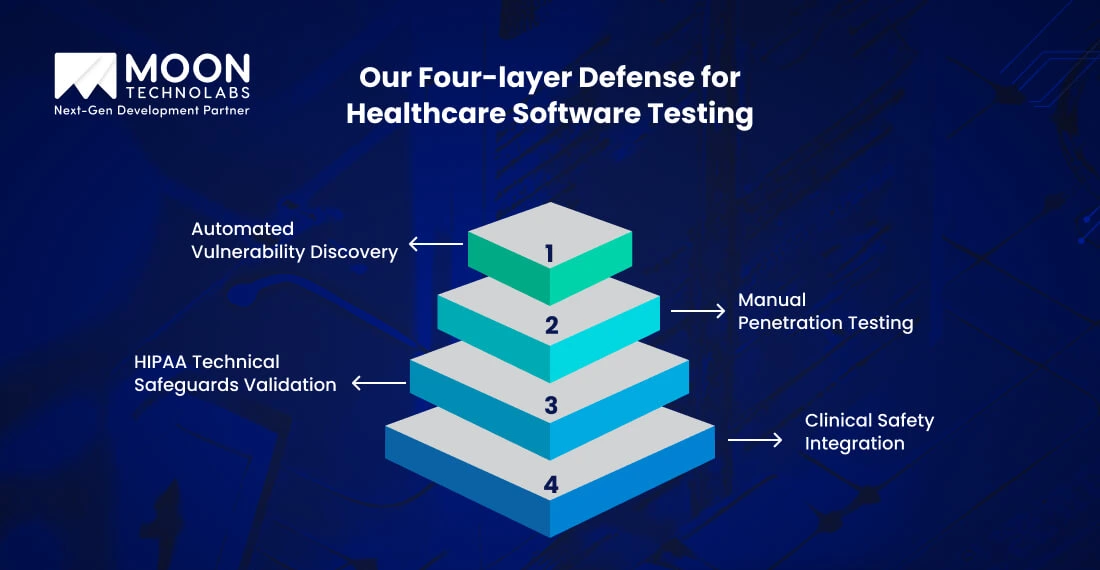
Layer 1: Automated Vulnerability Discovery
Our security testing begins with sophisticated automated tools that scan for surface-level vulnerabilities 24/7. Using industry-standard platforms like OWASP ZAP and specialized healthcare security scanners, we identify obvious security gaps before they become patient safety risks.
While automated tools are highly effective for detecting surface-level vulnerabilities, manual testing remains essential for complex scenarios that require deeper analysis and human judgment.
Layer 2: Manual Penetration Testing
This is where human expertise becomes irreplaceable. Our certified ethical hackers think like malicious actors, exploring creative attack vectors that automated tools miss. Regression testing is also essential after applying security fixes, as it helps confirm that no new vulnerabilities have been introduced and that previous issues remain resolved, ensuring robust test coverage.
Layer 3: HIPAA Technical Safeguards Validation
Every healthcare app must implement the 12 HIPAA technical safeguards, from unique user identification to audit trail mechanisms. Software requirement analysis plays a crucial role in ensuring all technical safeguards are properly specified, testable, and compliant with relevant standards.
We verify it’s implemented correctly, tested under stress, and maintained throughout the application lifecycle.
Layer 4: Clinical Safety Integration
Healthcare security testing isn’t complete without understanding clinical workflows. We collaborate with healthcare professionals to ensure security measures don’t interfere with life-critical decision-making. Usability testing is essential to confirm that security features are intuitive and user-friendly, so they support rather than hinder clinical workflows.
Discover the security gaps that 90% of healthcare apps miss with our specialized vulnerability assessment consultation.
Our functional QA templates serve as patient safety blueprints, transforming complex healthcare workflows into systematic, testable scenarios that protect both clinical outcomes and personal privacy. Testing healthcare applications is crucial to ensure the quality and safety of medical software, as it meets the high standards required in the healthcare industry.
Each test case in our template includes traceability fields that connect specific functional requirements back to clinical workflow documentation and regulatory compliance standards.
We actively involve healthcare providers in the testing process to ensure that the needs and insights of these professionals are addressed, improving the usability and effectiveness of medical software. Every upload test case includes automatic PHI detection checks to ensure no real patient information accidentally enters our testing environment.
Our templates dig deeper into the human reality of healthcare. We test scenarios like:
Our patient report upload templates go far beyond testing “different file types.” We simulate real-world scenarios using carefully crafted mock data that maintains absolute patient confidentiality while testing critical edge cases:
Ensuring data accuracy in these scenarios is crucial for validating test results and ensuring reliable outcomes, particularly when handling sensitive patient information and critical healthcare processes.
Our UAT sign-off template reflects the actual accountability structures in healthcare. In a healthcare organization, oversight and approval of the UAT process are essential to ensure compliance, patient safety, and operational efficiency. Our template ensures:
Layer 1: Clinical Workflow Validation
Product teams verify that features align with actual patient care processes, tested with diverse user personas representing different medical specialties and experience levels. Additionally, they ensure compatibility and integration with the overall healthcare system, validating that new features work seamlessly within the comprehensive digital infrastructure supporting patient care.
Layer 2: Technical Integration Verification
Dev/QA teams confirm seamless EHR (Electronic Health Records) synchronization, ensuring patient data integrity across all connected systems while maintaining optimal performance. Streamlined integration testing helps reduce testing time, enabling faster releases and greater efficiency.
Layer 3: Granular Action Logging
Compliance teams conduct final privacy checks, verifying zero PHI exposure in logs and confirming all audit trail mechanisms function correctly under stress conditions. Compliance testing can significantly impact overall testing costs, making efficient processes essential to keep expenses manageable while ensuring regulatory standards are met.
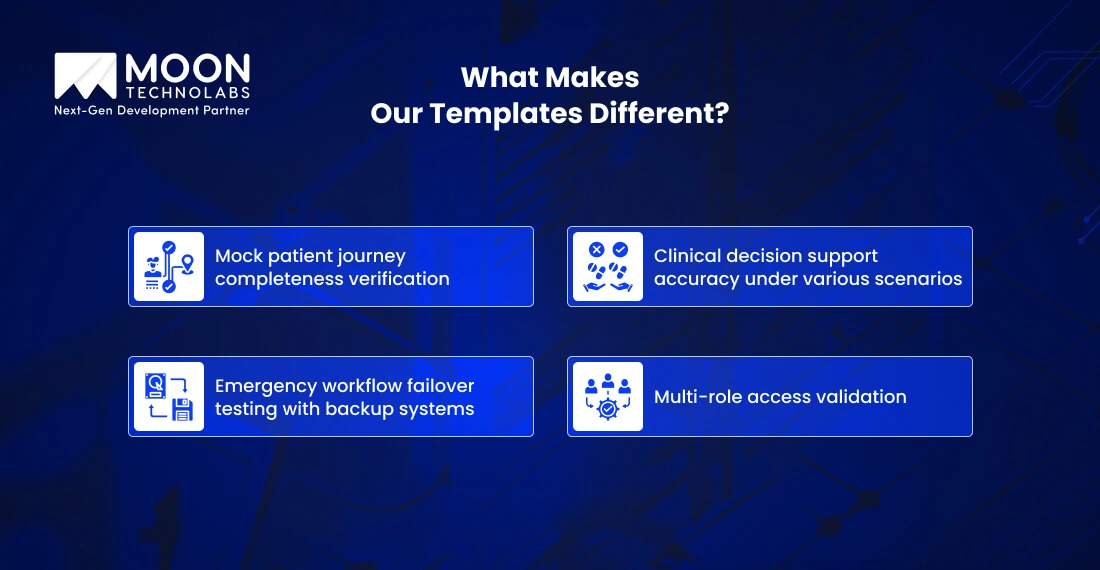
Each template includes healthcare-specific validation checkpoints that standard QA processes miss:

We build incident response systems that are capable of detecting unusual activities. These could range from a user account in a pediatric telehealth app that accessed thousands of patient records in just under 30 minutes.
The automated alert immediately pings our security team via Slack, while simultaneously creating a comprehensive audit trail that would later prove invaluable during the ensuing investigation.
To ensure comprehensive coverage, we also incorporate mobile app testing into our audit trail and incident alert systems, verifying that both desktop and mobile environments are monitored effectively.
Sometimes these aren’t malicious breaches; they were from an exhausted resident physician using a workaround to batch-download patient files for morning rounds. However, without a robust audit trail system, it can trigger a catastrophic investigation into a HIPAA violation.
Pillar 1: Granular Action Logging
Every sensitive healthcare action generates detailed, immutable log entries. Whenever a patient’s reports are uploaded, our system captures not just what happened, but when, where, how, and why. This also includes the device fingerprint, network location, and clinical context that justified the access.
Pillar 2: Real-Time Anomaly Detection
Our alert system goes beyond simple threshold monitoring. We utilize behavioral analytics to comprehend typical usage patterns for various healthcare roles. Whether nurses suddenly want to access cardiology records after months of working exclusively in pediatrics, our system triggers immediate investigative protocols.
Pillar 3: HIPAA-Compliant Storage Architecture
Audit logs themselves contain sensitive information. Hence, we implement triple-encrypted storage with automated backup retention spanning seven years, exceeding HIPAA’s six-year requirement. Each log entry is cryptographically signed to prevent tampering, ensuring forensic integrity during regulatory audits.
Pillar 4: Incident Response Orchestration
When unusual activity is detected, our documented incident response plan activates automatically:

Healthcare apps require bulletproof traceability, robust error handling, and instant notification for every risk vector. Hence, selecting the right methodology is crucial to incorporate deep clinical context, rigorous regulatory oversight, performance testing, and advanced cloud monitoring.
Our team recently faced a complex security and reliability challenge when a telehealth client reported missing audit log entries and random session drops during virtual consultations. Every lost entry or session could mean gaps in patient safety documentation, regulatory exposure, and disrupted care delivery.
The client’s platform was experiencing intermittent failures:
Step 1: Root Cause Analysis with Advanced QA Toolkit
We began with exhaustive analysis using our specialized functional QA templates and incident tracking dashboards. By correlating log files, network traces, and simulated user traffic, we pinpointed the failure: API timeout and race conditions in the audit logging path.
Step 2: Intelligent Retry Logic Implementation
Instead of basic error-handling, we architected a smart retry protocol in the audit logging system. Whenever a logging request failed (due to network, server load, or software errors), our system would automatically retry up to three times with exponential backoff.
Step 3: Real-Time CloudWatch Alerts and Continuous Monitoring
Integrated CloudWatch real-time alerting, configuring metrics for dropped sessions, missing log events, and abnormal access patterns. This provided instant visibility and triggered automatic notifications to our security analysts and DevOps, enabling rapid response and remediation.
Step 4: Post-Fix Interoperability Testing
We used our interoperability test templates to ensure that audit and session data remained consistent across EMR, appointment scheduling, and telehealth modules. This guaranteed end-to-end traceability and prevented clinical data silos.
Enhance your healthcare app’s security posture with our comprehensive incident detection and response framework, specifically designed for clinical environments.
When leading healthcare startups and enterprises approach us, we often discover various things that their security processes overlook. It could range from a critical SQL injection vulnerability to the exposure of PHI log files.
Healthcare testing is a comprehensive process that ensures the safety, security, and interoperability of healthcare software applications. By leveraging automation tools and test automation, we enhance both the efficiency and security of our testing workflows, supporting various testing types and reducing manual effort.
However, our comprehensive security tool stack is always ready to face real-world challenges. Within 48 hours of deployment, our integrated security testing platform is capable of uncovering critical vulnerabilities.
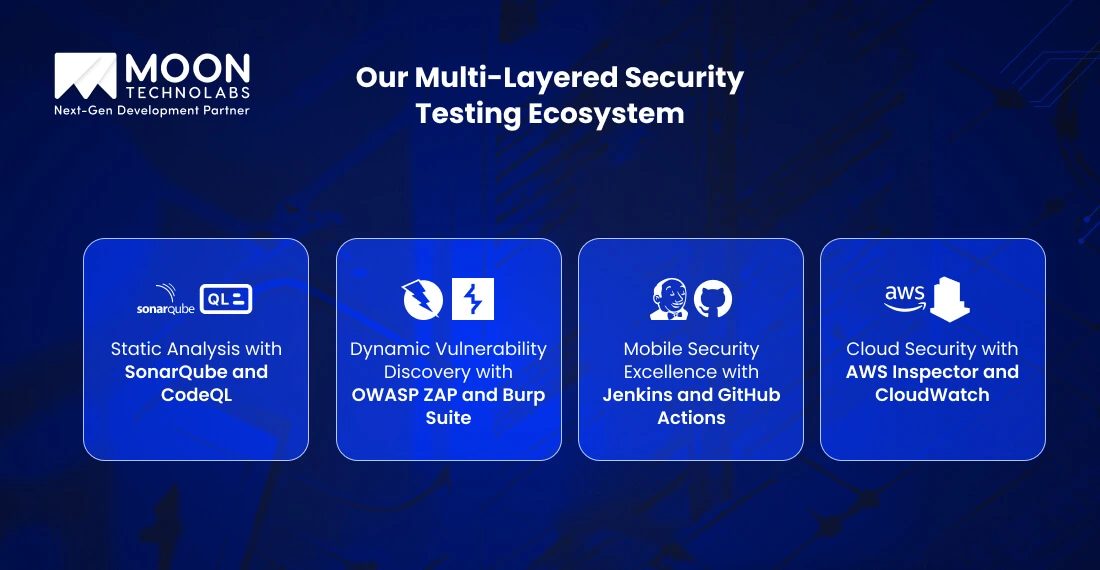
Our SonarQube and CodeQL integration performs deep static analysis that goes beyond surface-level scanning. While competitors like Testlio rely on basic automated scans, we’ve customized our static analysis rules specifically for healthcare applications.
Our CodeQL queries detect healthcare-specific vulnerabilities, such as PHI exposure in log files, hardcoded FHIR API keys, and insecure patient data serialization.
OWASP ZAP and Burp Suite form the backbone of our dynamic analysis, but it’s our healthcare-specific configuration that sets us apart. We’ve developed custom Burp Suite extensions that understand FHIR APIs, HL7 message structures, and DICOM protocols.
Rather than testing healthcare apps with generic web application scanners, our specialized tools consistently catch medical device communication vulnerabilities.
Our mobile security framework (MobSF) deployment includes healthcare-specific modules that test for medical device Bluetooth vulnerabilities, encrypted health data storage compliance, and FDA mobile medical app requirements. We don’t just test if an app works—we verify it meets the unique security standards that healthcare demands.
Our Jenkins and GitHub Actions pipelines automatically trigger comprehensive security scans with every code commit. However, what sets us apart is our comprehensive pipeline, which includes HIPAA compliance validation, clinical workflow integrity checks, and medical device interoperability testing—all conducted in parallel with traditional security scans.
AWS Inspector and CloudWatch alerts provide real-time monitoring, but our healthcare-specific cloud security goes further. We’ve implemented blockchain-based audit trails for critical patient data transactions, ensuring tamper-proof compliance documentation that exceeds both HIPAA requirements and FDA medical device software validation standards.
Healthcare mobile app security is a high-stakes challenge where every overlooked vulnerability can have devastating consequences. Drawing on real-world scenarios, competitor insights, and our methodologies, we have identified key lessons learned.
We also cover some common pitfalls and how our best practices and templates help healthcare organizations thrive in compliance, patient safety, and operational resilience.
Scenario: In an emergency room, a doctor faced a healthcare app with a hidden security flaw that was discovered weeks too late. It led to the exposure of thousands of patient records to hackers, who silently monetized the data on the dark web. This illustrates the dangers of skipping deep, continuous security testing.
Best Practice: We implement proactive scripting and automated vulnerability scanning integrated into continuous integration (CI) pipelines. Every code commit triggers layered static and dynamic scans to catch potential exploits early and often, preventing “digital doors left wide open.”
This approach surpasses generic scans used by some competitors by tailoring tests to healthcare protocols and clinical data flows.
Scenario: A simple coding oversight can expose sensitive patient data through an insecure API endpoint, leading to identity theft and substantial financial losses. Behind this is a failure to maintain comprehensive audit trails and real-time monitoring.
Best Practice: Our custom audit trail templates and real-time incident alerting ensure every data access is logged with clinical context, storing immutable logs for HIPAA and FDA audit readiness.
Unlike many frameworks that overlook traceability, our solutions provide comprehensive audit lifecycle management, including automated notifications of anomalies to help close gaps.
Scenario: The 2024 Change Healthcare ransomware attack compromised 190 million records through a Citrix portal. The portal lacked MFA, a simple security feature that could have averted the breach.
Best Practice: We embed MFA and zero-trust principles into security testing workflows and verify their proper implementation during penetration tests. Our approach mirrors that of top US competitors, but we also incorporate clinical safety checks to ensure these controls never interfere with emergency access scenarios.
Scenario: An app can unknowingly expose GPS data, violating HIPAA and resulting in a hefty fine. It’s similar to one of the high-stakes cases involving the Munich clinic, which faced GDPR fines for unclear AI data consent.
Best Practice: Our healthcare-specific compliance fields in QA/UAT templates explicitly validate privacy impact, consent handling, and data minimization in all workflows. We help teams avoid regulatory pitfalls by embedding these checks early and throughout development, in contrast to competitors whose generic forms lack such granularity.
While many US competitors provide automated or manual security testing services, our distinction lies in the integration of proactive scripting, real device testing across diverse healthcare environments, regular CI audits with compliance validation, and a deep understanding of clinical safety needs.
Our methods do not treat security and QA as checkbox exercises but as continuous, adaptive patient safety imperatives. By combining thorough technological rigor with healthcare-specific contextualization, our practices reduce risk, prevent costly breaches, and support uninterrupted, safe care delivery.
We reinforce that robust healthcare app security requires continuous vigilance, tailored templates, integrated compliance management, and real-time monitoring. These elements transform QA from a routine process into an unbreakable shield for patient safety, regulatory certainty, and operational excellence.
01
02
03
04
Submitting the form below will ensure a prompt response from us.