Table of Content
Blog Summary:
The blog explores the key differences and benefits of IoT vs IoT, highlighting how these technologies are transforming industries and daily life. IoT focuses on enhancing consumer convenience through smart devices, while IIoT drives industrial efficiency with advanced systems. Partnering with experts like Moon Technolabs ensures seamless implementation and maximized benefits.
Table of Content
The Internet of Things (IoT) operates by collecting data from the environment through sensors. By transmitting it to cloud platforms for processing, IoT uses the insights to trigger automated actions or provide feedback to users.
These IoT devices, embedded with sensors, software, and other advanced technologies, include smart home appliances like refrigerators and thermostats. However, they also extend to applications in the manufacturing industry, such as wearable fitness trackers, known as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
Industrial IoT focuses on optimizing industrial operations in sectors such as manufacturing, energy, and healthcare, enhancing production efficiency, and reducing downtime. Similarly, IoT primarily addresses consumer needs by enabling automation, improving decision-making, and enhancing user experiences.
Understanding IoT vs IIoT is the key to their accurate application. This blog will explore how IoT and IIoT bridge the gap between the digital and physical worlds.
Interconnected devices create the Internet of Things. These devices range from simple household items like light bulbs to advanced systems like smart cars. IoT lets these devices collect, send, and analyze data to automate processes.
For instance, a smart thermostat can learn your temperature preferences and adjust itself accordingly, saving energy and enhancing comfort. IoT is essentially about making our lives more convenient and efficient by connecting the things around us.
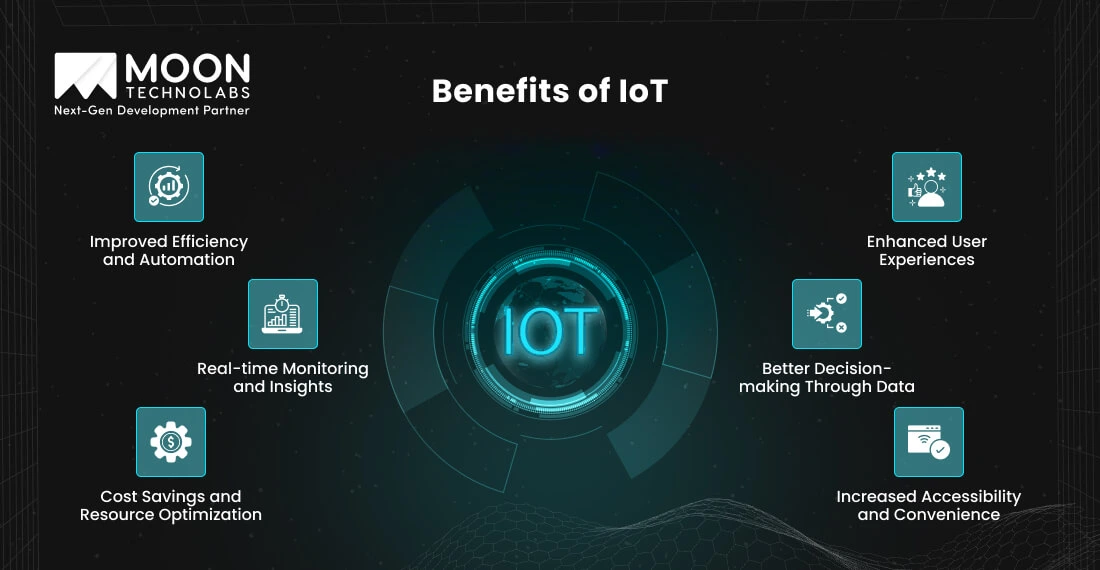
The Internet of Things (IoT) offers numerous advantages by connecting smart devices and systems, enhancing everyday convenience and operational efficiency across various sectors.
IoT automation minimizes manual labor and increases efficiency. Devices like robotic vacuum cleaners, intelligent lighting systems, and automated production lines in factories showcase how IoT simplifies operations. By minimizing human error and optimizing processes, IoT ensures smooth workflows and enhances productivity across various domains.
IoT allows real-time device and system monitoring. This capability is crucial in industries like healthcare, where wearable devices monitor patients’ vital signs, alerting doctors to any abnormalities. Similarly, smart home security systems provide instant notifications of potential breaches, ensuring prompt responses.
IoT facilitates resource optimization, leading to significant cost savings. For instance, smart thermostats adjust heating and cooling based on occupancy, cutting down on energy bills. In industrial settings, IoT-enabled predictive maintenance helps avoid costly breakdowns by identifying potential issues before they escalate.
IoT improves user experiences by providing customized and intuitive interactions. Voice assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Home allow seamless control over connected devices, from playing music to adjusting room temperature. This integration enhances convenience and fosters a tech-savvy lifestyle.
IoT devices collect and analyze data for insights. Businesses leverage this information to refine their strategies, improve customer experiences, and streamline operations. For example, retail stores use data from IoT sensors to track foot traffic patterns and optimize product placement with smart inventory management systems.
IoT enhances accessibility, particularly for individuals with disabilities. Smart homes equipped with IoT devices allow users to control lights, doors, and appliances through voice commands or mobile apps.
You Might Also Like:
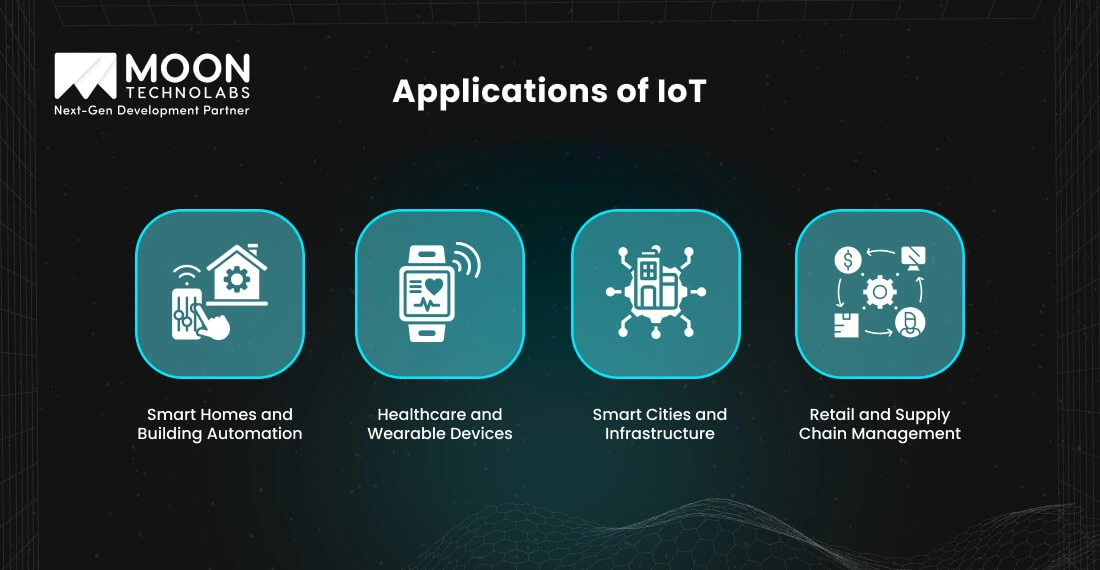
The IoT has revolutionized numerous sectors by integrating smart devices and advanced technologies, leading to enhanced efficiency and improved user experiences. IoT applications are changing our environment, from smart homes to healthcare.
Smart devices have revolutionized residential spaces by enabling smart home automation. Smartphones can control security cameras, thermostats, and lighting, improving home comfort, energy efficiency, and security.
IoT in healthcare has led to significant advancements in the sector. Wearable devices such as smartwatches and fitness trackers monitor heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity. IoT also supports telemedicine, allowing patients to consult doctors remotely and receive timely medical care.
IoT is a cornerstone of innovative city initiatives, addressing urban challenges like traffic congestion and pollution. Data transmission is crucial in these systems to ensure the reliability of real-time updates and optimizations.
Connected traffic systems optimize signal timings to reduce jams, while IoT-enabled waste management systems streamline garbage collection based on bin levels.
IoT helps retailers enhance customer service and efficiency. Smart shelves equipped with weight sensors notify staff when stock levels are low. IoT in supply chains enhances shipments tracking in real time, ensuring timely deliveries and minimizing disruptions.
The IIoT connects machinery, sensors, and software to optimize operations, enhance safety, and reduce costs. IIoT is integral to industries like manufacturing, energy, and transportation, where reliability, scalability, and robust security are paramount.
Unlike consumer IoT, which prioritizes convenience, industrial IoT applications emphasize operational efficiency and safety.
For instance, a power plant may use IIoT sensors to monitor equipment performance, predict failures, and schedule maintenance, ensuring uninterrupted service and reducing downtime.
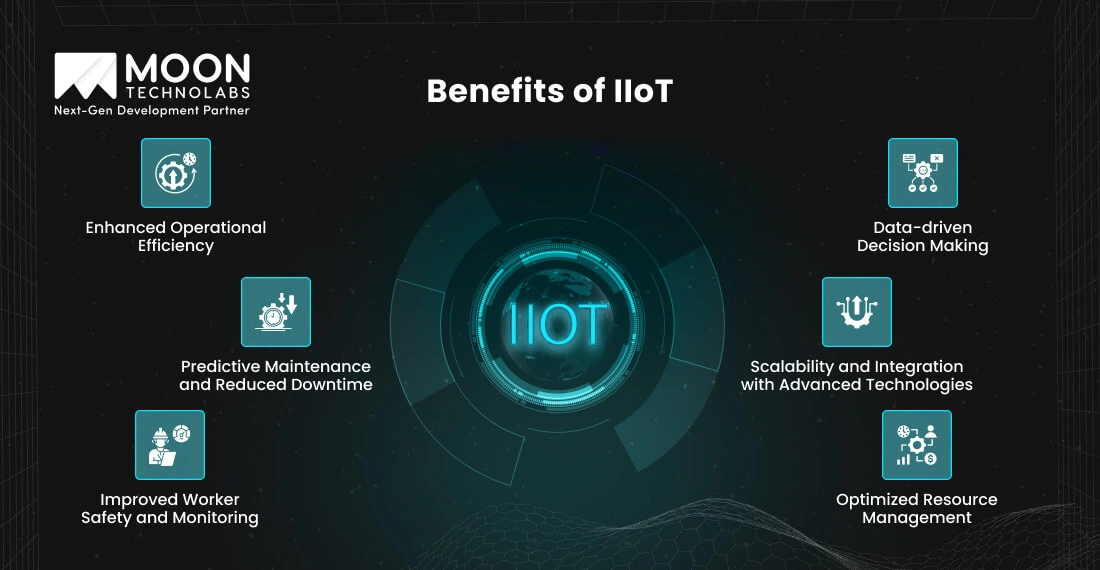
The IIoT offers transformative advantages for industrial environments. Through smart technology integration, it enhances operational efficiency and safety while driving cost reductions.
IIoT automates repetitive tasks and streamlines workflows, boosting productivity and reducing operational costs. Connected systems ensure seamless communication between machines, optimizing industrial processes and minimizing waste.
By continuously monitoring equipment and performance, IIoT provides real-time data that helps identify inefficiencies and rectify them quickly. This leads to smoother operations and a reduction in the time spent on manual oversight.
Predictive maintenance is a significant IIoT benefit. By analyzing sensor data, IoT systems can identify potential equipment failures before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance.
This minimizes downtime and prevents costly disruptions. Additionally, predictive maintenance can extend the lifespan of machines, improving the return on investment for equipment and contributing to the overall reliability of operations.
IIoT monitors worker health and environmental parameters to improve workplace safety. For example, wearable devices can detect hazardous gas levels in chemical plants and alert workers to evacuate.
This technology ensures a safer work environment and reduces the risk of accidents. Furthermore, remote monitoring of workers’ physical health, such as heart rate or body temperature, can detect fatigue or health issues early for timely intervention.
Integrating industrial systems with IIoT provides industries with valuable insights into their operations by analyzing data from connected devices. It allows businesses to make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and adapt to market changes.
This data-driven approach enables strategic planning and long-term growth. Additionally, it allows organizations to identify areas for continuous improvement, monitor supply chain performance, and adjust manufacturing processes based on real-time feedback.
IIoT systems are highly scalable, allowing industries to integrate emerging technologies like AI and robotics. This adaptability ensures that businesses can keep pace with technological advancements and remain competitive.
As the scale of operations grows, IIoT systems can be easily expanded to accommodate additional sensors, devices, or machinery, enabling seamless integration and future-proofing the business.
Industrial IoT optimizes resource use, minimizing waste and expenses. For example, smart energy grids monitor electricity demand and adjust supply accordingly, ensuring efficient energy distribution.
IIoT also allows companies to track raw material usage, minimize waste, and optimize smart inventory management systems. By offering real-time visibility into resource consumption, businesses can reduce overhead costs and enhance sustainability efforts.
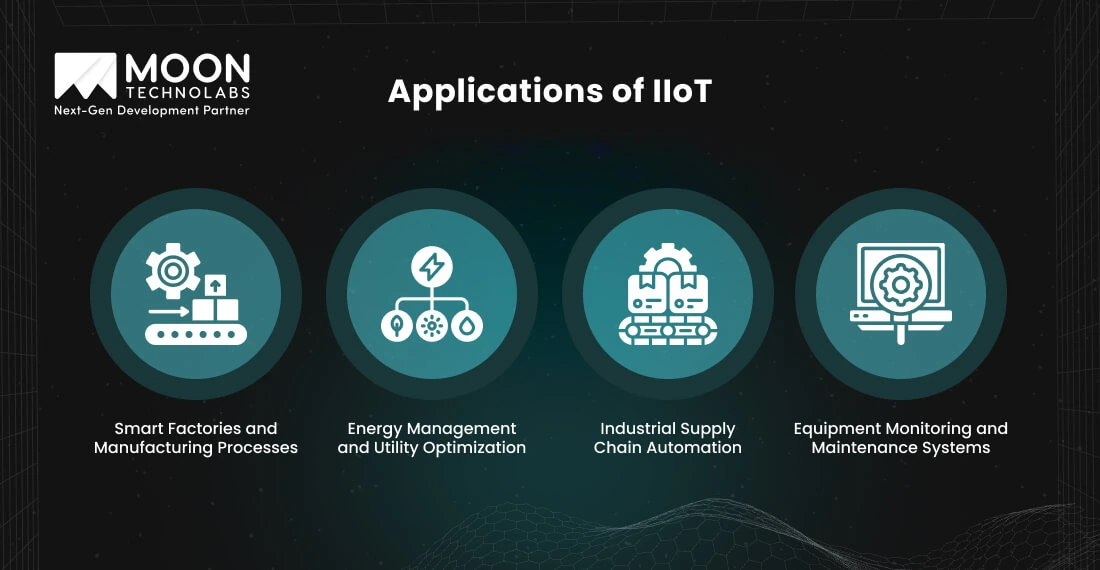
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is transforming industrial environments by integrating smart devices and advanced technologies to optimize operations and enhance efficiency. From smart factories to energy management, IIoT applications drive innovation across various industrial sectors.
IIoT enables the creation of smart factories, where interconnected systems automate production lines, monitor equipment, and maintain quality control. This improves product quality, productivity, and error reduction.
Industrial energy optimization relies on IIoT and IoT technology. By monitoring and analyzing energy consumption patterns, IIoT systems identify inefficiencies and implement corrective measures, reducing costs and improving sustainability.
IIoT automates inventory management and logistics. This automation ensures accuracy, reduces delays, and enhances overall supply chain efficiency, benefiting both businesses and consumers.
IIoT systems continuously monitor the performance of industrial equipment, detecting anomalies and scheduling maintenance before issues escalate.
Machine learning plays a crucial role in enhancing these systems by processing and responding to the data collected. This proactive strategy extends equipment life and lowers costs.
IoT enhances everyday connectivity, while IIoT revolutionizes industrial operations with advanced automation, real-time data, and system integration. They both drive efficiency and productivity in manufacturing and supply chain management in different ways. Let’s understand the core distinctions between both of them.
| Feature | IoT | IIoT |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose and focus area | Consumer convenience | Industrial optimization |
| Devices and Connectivity | Smart home devices, wearables | Industrial machines, sensors |
| Data Handling and Analytics | Moderate | Massive |
| Security Requirements | Basic | Advanced |
| Examples in Practice | Smart homes, fitness trackers | Factories, energy plants, logistics |
You Might Also Like:
Moon Technolabs Ranked as Top IoT Developers in USA by Techreviewer
Whether you are looking to develop smart home systems or implement advanced industrial networks, we deliver cutting-edge technology and unparalleled expertise. By partnering with us, you gain access to IoT and IIoT solutions that drive innovation and improve efficiency.
At Moon Technolabs, we ensure a seamless and successful implementation of IoT and IIoT. We are a leading IoT Development Company specializing in providing comprehensive IoT and IIoT solutions tailored to your unique business needs:
Connect with our IoT experts today to develop smart interconnected systems and automate your business processes.
Understand how IoT and IIoT can be the game-changer your business needs for a competitive edge.
IoT improves consumer convenience, while IIoT transforms industrial operations. The difference between the two lies in their focus: IoT enhances everyday consumer experiences, while IIoT drives efficiency and productivity in industrial environments.
Both technologies offer transformative benefits, from improved efficiency and cost savings to real-time insights and enhanced user experiences. As they progress, the potential for innovation and improved quality of life grows exponentially.
01
02
03
04
05
Submitting the form below will ensure a prompt response from us.