Table of Content
Blog Summary:
This guide offers a comprehensive and practical overview of data interoperability in healthcare, emphasizing its pivotal role in EHR (Electronic Health Record) testing and its impact on the flow, security, and utility of health data. The blog will explain interoperability concepts, industry standards, best practices for EHR interoperability testing, major implementation challenges, and actionable solutions. It will also serve as a strategic resource for healthcare technology stakeholders seeking to achieve seamless, secure, and regulatory-compliant data exchange.
Table of Content
Healthcare organizations invest millions to empower clinicians with real-time patient data. However, data interoperability in healthcare remains a significant challenge, often resulting in delays, redundant diagnostics, and fragmented care delivery.
Let’s take an example of an ordinary morning in a hospital. A cardiologist waits anxiously for critical ECG data to finalize a patient’s treatment plan. While the lab uploaded the report, the hospital’s system failed to process it due to incompatible formats. This led to wasted hours and delayed treatment plans.
For healthcare organizations, this isn’t an isolated technical glitch; it indicates underlying interoperability gaps and risks that threaten organizational efficiency and care delivery. That’s why data interoperability in context-aware EHR testing is crucial for connecting healthcare practices with other existing systems.
It verifies that data is exchanged and interpreted accurately, as well as validated across systems for actionable care, powered by fully defined data-sharing standards, such as HL7, CCD, and FHIR. In this guide, you will learn the fundamentals of EHR testing along with a walkthrough of real-world testing strategies to incorporate interoperability in practice.
Interoperability refers to the ability of different health IT systems and software to access, exchange, and interpret patient data in a standardized and well-defined manner.
Consider a situation where a patient visits multiple specialists, each using a different EHR system. The absence of seamless data exchange results in delayed diagnoses, repeated treatments, and a poor patient experience.
That’s why data interoperability is important for your healthcare systems. It doesn’t just involve sending files back and forth; it enables you to access data that is accurate, consistent, and usable across systems.
You can provide faster, safer, and personalized care to your patients with interoperability at the core of your system. As providers, you gain a complete view of the patient’s medical history, which enables smarter decisions while minimizing redundant tests. It also empowers your team to collaborate in real-time, leading to better outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
Interoperability is not just an option for you; it is a regulatory mandate that ensures improved data flow and care. There are initiatives, such as the 21st Century Cures Act. Under this act, your healthcare organization must support standard data and eliminate information blocking. By adhering to compliance, you can stay aligned with federal mandates while providing a more connected and value-based care model.
EHR data interoperability, as a backend issue, impacts everything, from how quickly patients are diagnosed to the seamlessness with which care transitions occur between providers.
As a result, your healthcare systems, clinics, and even their apps can communicate with each other in a language everyone understands. Let’s look at the key pillars that make interoperability a reality:
Each level in the layered interoperability is built upon the others to provide a seamless experience for all stakeholders.
In this basic interoperability layer, you will find that one system can exchange data with the other. However, the receiving system may not be able to interpret the data fully. It is akin to the email containing information and documents that you send to another person; you have passed the information, but you cannot interpret it for them.
The second level defines how data is formatted and organized during the exchange. In this layer, you will notice consistency at its core, which helps systems process information without manual intervention. It incorporates the standard message structures, such as HL7 formats, to improve data exchange.
It takes data exchange to the next level by preserving the meaning and helping the stakeholders interpret it accurately. Standard terminologies, such as SNOMED (Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine) and LOINC (Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes), are used in this layer to enable systems to interpret context as intended.
With this layer, your systems move beyond technical exchange. It helps align policy frameworks, data-sharing agreements, workflows and security protocols for data privacy. With this, healthcare entities can collaborate effectively in real-world settings.
Using standards, you can establish a common language for the different systems. HL7 (Health Level Seven) is a foundational framework that has been in use for decades, helping different systems communicate using a structured language.
FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) is built on HL7 and introduces a more modern, web-friendly approach to using RESTful APIs. You can use this standard when building health apps or cloud platforms.
Lastly, the Continuity of Care Document (CCD) sends across patient snapshots that are useful during care transitions.
These standards are crucial in making interoperability consistent, scalable, and a reality across vendors and systems.
You can share a range of data, including patient demographics, medication lists, allergy records, lab results, and diagnostic images, with interoperable systems. Additionally, you can also exchange clinical notes, discharge summaries, and billing/insurance information with them.
Every piece of data you exchange contributes to creating a more accurate view of the patient, enabling care providers to make well-informed decisions.
Testing data interoperability in EHR is a separate focus area to consider. With general healthcare app testing, you focus on user interface, functionality, and performance.
However, with EHR testing, your focus shifts towards integrity and flow of critical healthcare data across diverse systems. That’s where you need to prioritize interoperability.
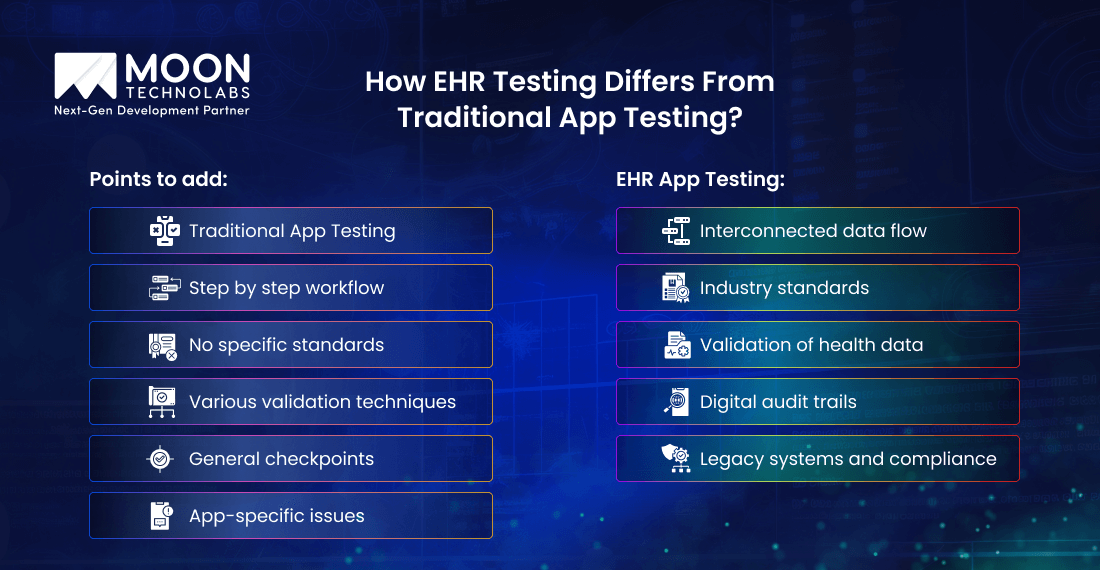
Most healthcare apps you develop operate in silos. However, EHRs are at the core of a highly connected healthcare ecosystem. Since they interact with labs, pharmacies, imaging systems, and even public health databases, health records management is one of the must-have features of an EHR.
Hence, you cannot use generic app testing to analyze these complex touchpoints.
With EHR testing, your primary focus is on integration points, data accuracy, workflow alignment, and compliance with healthcare data standards. This helps you create a more structured and defined data movement that is seamless and efficient.
Integration, data migration, and interface/API testing are the three specific areas that must be tested for interoperability in EHR.
In short, you use EHR testing to verify interoperability, enabling healthcare systems to support efficient data exchange for real-world and high-stakes applications.
Consult with our experts to design a testing strategy that adheres to compliance, minimizes risk, and enhances real-world outcomes.
Start Testing Now
EHR interoperability test helps you validate that the data is transported safely and accurately between systems. These best practices can help your QA and integration teams stay ahead of the demands for compliance and complexity.
When conducting interoperability testing, it is essential to have a detailed and clear requirement analysis. This should include the expected data flows, identification of third-party systems, and the compliance requirements of your system.
Once you have the requirements in place, you should begin creating realistic test data cases that mirror clinical workflows. Don’t test the isolated endpoints alone; instead, simulate the entire journey by creating scenarios for referrals, lab orders, and patient discharges.
Using these scenarios, you can identify the breakdowns and issues within the journey.
Your tests should verify that the data remains intact, complete, and properly mapped when moving between systems. It includes validating terminologies such as SNOMED and ICD-10, while also ensuring that no data fields are excluded when data transitions between systems.
You should include edge cases, such as code mismatches, null values, and versioning conflicts, in your testing. While they are rare, their occurrence during data movement can lead to delayed treatment or compliance issues.
You can improve resource utilization effectively with automation to enable consistent data flow across loads. Here’s how:
Automation helps monitor the scripts after deployment, flagging and solving interoperability failures in real-time. Automation isn’t a substitute for manual testing. It helps speed up and continuously validate the systems while allowing manual resources to focus on core jobs.
Your testing suite should include checks for data blocking rules, API conformance, and privacy measures outlined by HIPAA and ONC. Your goal shouldn’t be limited to passing audits; it should include ensuring systems behave responsibly in live environments.
With a compliance-focused test suite, you can build systems that aren’t just functional, but also credible and transparent.
Explore our EHR testing services designed to validate the APIs, streamline data exchange and ensure compliance with ONC & FHIR standards.
Talk to Our Specialists

While making EHRs interoperable sounds great in theory, it isn’t as easy in practice. You face several roadblocks while establishing interoperability. Let’s look at some of the biggest challenges you are likely to encounter.
The biggest issue you will face is a technical and workflow silo. Each department uses a different system that doesn’t communicate naturally.
Owing to a lack of integration, you will notice duplicate data entry, misaligned care coordination, and several bottlenecks. This restricts the flow of data across facilities and care settings.
Many hospitals and clinics rely on legacy EHR systems, which don’t conform to modern interoperability standards. There is no straightforward way to integrate them to modern platforms, such as a FHIR-enabled healthcare app.
If they include outdated data formats, custom interfaces, and missing documentation, you will notice that data exchange is messy and unreliable.
Even when you have the right tech but not enough trained people to use it, you will notice a slowdown. Clinicians are reluctant to adopt new systems, while IT teams are grappling with diverse priorities, which leads to resistance to change.
Security is crucial when dealing with healthcare data. You must ensure secure transfers and HIPAA-compliant access controls while moving data from one system to another.
You can put the patient’s privacy and the organization’s reputation at risk if you find a misconfigured API, unauthorized access, or unaccounted vulnerabilities while testing.
Solving the EHR interoperability and testing challenges isn’t a one-time fix. It is a continuous effort to build smarter and connected systems from scratch, enabling healthcare organizations to stay ahead.
Here are all the ways to resolve these issues by continuously stepping up.
By utilizing open standards such as FHIR, HL7, and SMART on FHIR, you can establish a common language for systems to exchange data. These frameworks help simplify integration and reduce custom work, making it easier for EHRs, labs, and third-party tools to communicate with one another.
By shifting to cloud-backed EHRs and modern API architecture, you can enable scalable and flexible systems. Using cloud-native systems, you can support real-time data exchange, remote access, and interoperability with external partners without increasing overheads.
With automated monitoring for APIs, data flows, and security, you can catch inconsistencies, failed transfers, and performance issues before they impact patient care.
Technology works only when people using it understand its abilities. That’s why you should invest in ongoing training for clinicians, admins, and IT teams. This will help them stay confident while using interoperability features and avoid resisting change.
Implement a scalable and repeatable framework for interoperability testing. You can include the common scenarios, edge cases, and compliance checks. You can automate as much as possible while including clinical validation to ensure accurate interpretation.
More than a mere technical goal, Interoperability lays the foundation for a more connected, efficient, and patient-centred care. Hence, you need a more robust and context-aware testing for developing EHR software to ensure smooth data exchange, improve clinical accuracy, ensure regulatory compliance, and enhance real-world usability.
From integration and migration to API conformance, you need to validate every layer of interoperability. With a thoughtful and well-executed testing strategy, you can prevent system breakdowns that impact patient outcomes.
If you need help navigating the complexity of EHR testing, consult with interoperability and testing experts. At Moon Technolabs, we fast-track implementation, avoid pitfalls, and build future-ready healthcare systems. Schedule a free consultation with our team today.
01
02
03
04
Submitting the form below will ensure a prompt response from us.