Table of Content
Blog Summary:
This blog serves as a guide to Testing Medical IoT Apps and covers all the necessary points that the QA team should be familiar with. From basics, we explain testing challenges, regulatory and compliance fundamentals, core QA approaches, best practices, pitfalls, and much more.
Table of Content
Testing Medical IoT Apps has become mandatory rather than optional in today’s connected healthcare world. The reason is that the majority of healthcare organizations nowadays leverage IoT software to redefine their operations.
A recent report reveals that 60% of healthcare organizations already use IoT in their important operations. Some of these cutting-edge devices include wearable ECG monitors, smart ventilators, and other advanced medical devices.
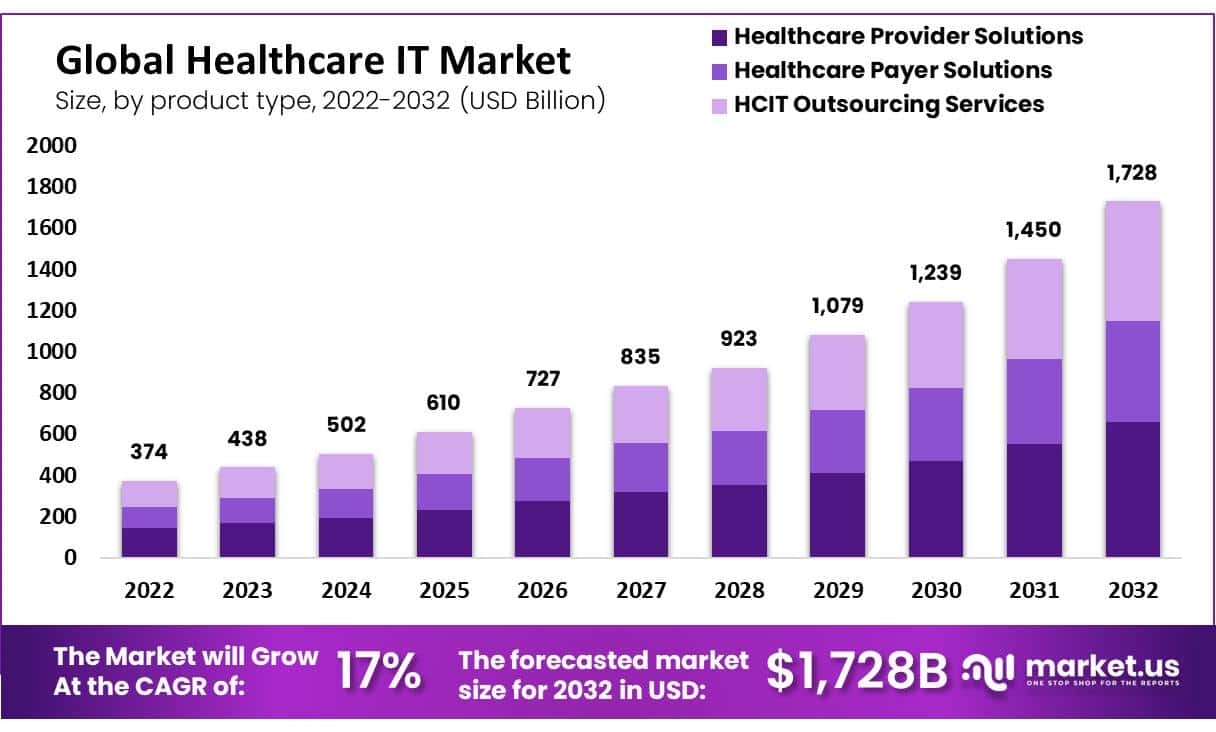
Meanwhile, it’s also true that great innovation comes with certain risks. According to recent statistics by Fortune Business Insights, 60% of IoT medical devices contain vulnerabilities.
On the other hand, many healthcare data breach cases have already been reported in connected devices. Even a broken data stream or a single faulty update causes unsafe dosing, misdiagnosis, or regulatory penalties.
All these factors increase the necessity of Internet of Things software testing for regulatory compliance, patient safety, and data integrity, in addition to functionality testing. This guide serves its ultimate purpose to assist IT leaders or QA teams in drafting strategies to validate connected devices.
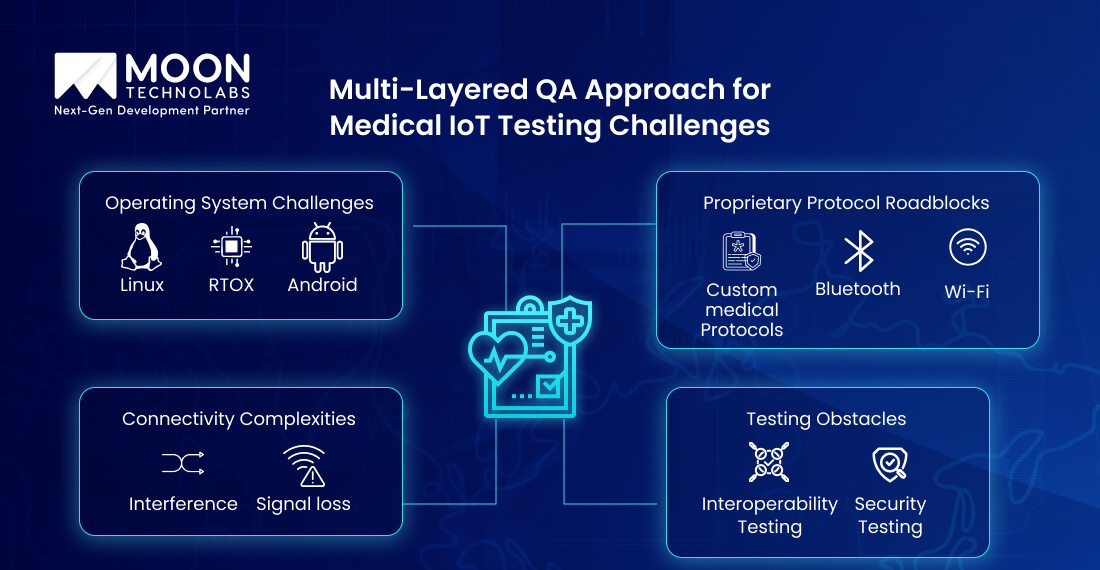
Medical IoT systems are complex, often accompanied by remote monitoring systems, diagnostic tools, and wearable devices. Due to this, the QA team faces numerous challenges that appear as follows;
Testing these layers often creates difficulties for QA teams without in-depth knowledge. It also causes data loss or undetected security flaws.
Many incidents have already taken place due to poor QA, resulting in device failure and compromised patient safety.
One of these incidents occurred in 2020, when the QA team failed to conduct testing of an insulin pump and thus couldn’t detect firmware issues. It resulted in improper dosage under low battery conditions. It created an emergency for diabetic patients.
Another incident occurred in 2022, when a remote heart monitor failed to sync with the arrhythmia due to OS-level incompatibility. As a result, it delayed intervention and missed emergency alerts.
For testing IoT medical apps, QA teams need to align their testing process with healthcare standards to ensure both legal accountability and patient safety.
HIPAA requires strict security and data privacy measures for protected health information (PHI). It reflects the verification of access controls, encrypted transmission, secure data storage, and more across various communication nodes.
It primarily applies to various medical devices that directly impact monitoring, diagnosis, treatment, and other related processes. It requires both developers and manufacturers to adhere to the guidelines of SaMD (Software as a Medical Device) frameworks, validation procedures, and risk categorization throughout the device lifecycle.
ISO 13485:2016 is another important regulatory standard that defines quality management systems in the development of various medical devices. It focuses on process validation, traceability, documentation, and other key aspects across the design, development, and testing phases.
Audit-readiness is crucial for a robust QA strategy in medical IoT. Below are some of its best practices:
A multi-layered QA approach is essential for complete testing of healthcare IoT software. It’s indispensable to maintain a perfect balance of automation with human insight, functional precision, simulation with real-world validation, and more.
Functioning testing is essential in healthcare IoT. It covers multiple aspects of input capture and device behavior, UI responsiveness, data transmission, alert mechanisms, and more. Manual testing is crucial for error handling, addressing edge cases, and ensuring compliance with features.
On the other hand, test automation is necessary for large-scale and repetitive validations, whether it’s sensor data parsing, API testing, or multi-platform UI regression. Tools like TestComplete, Appium, and Cypress automate the entire function flow.
Apart from this, non-functional testing is equally important. QA teams need to validate:
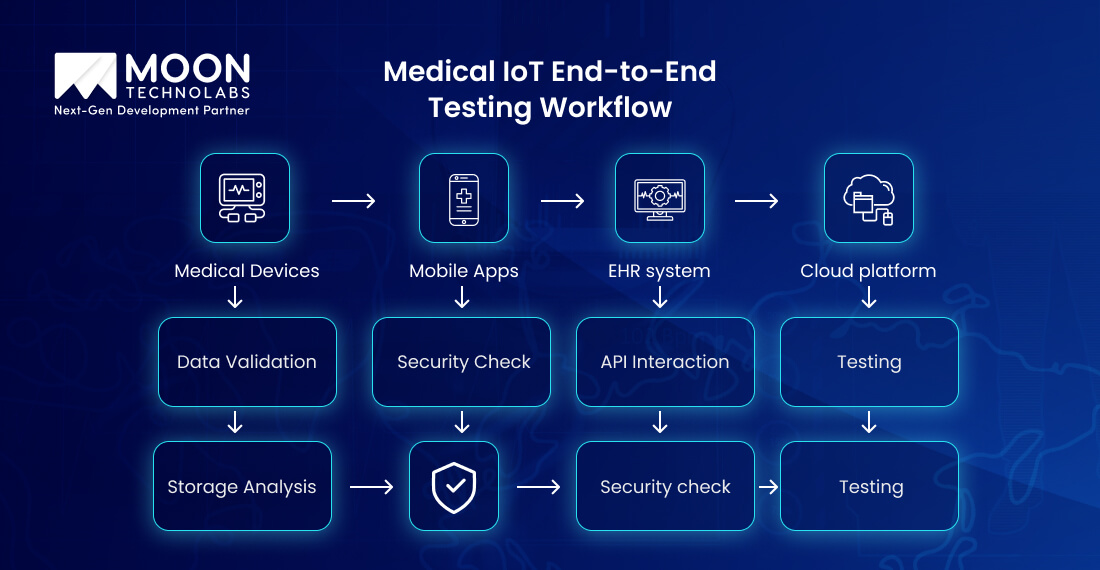
When it comes to medical IoT, it’s an important part of the connected ecosystem and involves the following important things;
When it comes to end-to-end testing, it ensures a secure data flow across the entire chain. It’s pivotal for QA engineers to validate the following important things;
Be it emulators or simulators, they are highly important in early-stage testing. Many tools, such as AWS IoT Device Simulator and custom firmware emulators, enable parallel and scalable testing even without the need for physical hardware.
Meanwhile, these tools are not capable of replicating hardware quirks, real-world interference, and battery degradation. That’s the reason why physical device labs are necessary for final-stage validation.
These labs allow:
A properly planned QA process combines simulation speed with real-device realism. It ensures medical IoT apps are not only code-complete but also clinically trustworthy.
We provide QA testing tailored for healthcare software for flawless performance while ensuring full compliance. Protect your patient matching HIPAA standards.
Consult Us Now
Security and data privacy are the backbone of medical IoT as they are essential for patient safety and also regulatory imperatives. Therefore, it’s essential to have a robust testing strategy to verify the security and data privacy of medical apps.
Penetration testing operates on the principle of simulating real-world cyberattacks to identify vulnerabilities in access pathways and data transmission. In a medical IoT system it involves:
The best part of penetration testing is that it gives you complete assurance that hackers can’t manipulate or intercept security systems or patient data.
Hence, there should be better coordination between security teams and QA to conduct regular penetration tests using several tools, such as Metasploit, OWASP ZAP, and Kali Linux, and document various remediation steps.
Medical IoT software should utilize end-to-end encryption for both at-rest (AES-256 or similar) and in-transit (TLS/SSL) data. The QA team should be capable of verifying the following important things;
The QA team should test multi-factor authentication and authentication protocols for token replay, brute-force attacks, and session hijacking to ensure their effectiveness. Additionally, secure provisioning should be properly verified to ensure that devices are not fully exploitable, especially during factory resets or initial setups.
Continuous vulnerability scanning places a higher importance on the evolving threats. To tackle it, QA experts need to integrate scanners into CI/CD pipelines.
Whether it’s Qualys, Nessus, or Synk, they can integrate these scanners to detect unknown vulnerabilities in device firmware, third-party libraries, and API gateways.
A thorough scanning helps you detect;
Healthcare IoT systems are designed to operate reliably even under pressure, with minimal downtime and data loss. Performance testing and reliability are essential for quality assurance, whether it involves syncing data across multiple devices or analyzing vital signs in real-time.
Latency is not only inconvenient but also dangerous, especially in remote ICU monitoring or cardiac telemetry. So, the QA team should verify IoT systems.
It also includes testing latency thresholds across BLE, LTE, and WiFi networks. It also simulates degraded connectivity to ensure auto-recovery and graceful degradation.
Loading tests are necessary to determine the overall performance under the anticipated traffic. On the other hand, stress testing involves pushing the entire system beyond its limits to recognize breaking points.
You can test the following scenarios;
Failover testing is necessary to automatically activate the backup system in the event of a regional outage or crash. This is indeed quite essential during emergency-care scenarios. The following are important tools that simulate high-concurrency conditions;
Distributed orchestration platforms are appropriate for large-scale testing. It allows QA teams to trigger, manage, and analyze tests across different environments and nodes. You can conduct various test cases at the same time across verified configurations by using the following tools;
Whether it’s Azure IoT Test Hub or AWS Device Farm, cloud-based platforms are capable of improving scalability. They also bring the possibility of parallel test execution across virtual and real devices.
QA teams adopt these strategies to ensure medical IoT systems are not only compliant but also secure. They are also resilient, scalable, life-critical, and reliable.
One of the major challenges in IoT software testing in healthcare is ensuring that multiple systems work in harmony. Interoperability does not just involve technical compatibility, but it also affects care continuity and clinical decision-making.
Healthcare IoT apps should ensure a smooth transition of data with higher accuracy and security across different layers:
Whether it is data transformation, mapping, or normalization, QA teams should test between every interface. For instance, a heart rate monitor sends signals in raw form.
And the app is responsible for converting it and displaying it in FHIR or HL7 format. It’s necessary to verify both accuracy and consistency at every step.
Medical systems rely on standards such as FHIR, HL7 v2, and DICOM to ensure interoperability. QA teams need to perform the following important things;
We help you make your medical app work smoothly with powerful QA. Our QA ensures your app is bug-free and highly secure.
Hire Our Services Today
A robust QA strategy of medical IoT apps relies heavily on regular awareness, consistency, and test coverage discipline. Still, the team commits certain mistakes that affect the compliance and safety of products.
You should have full preparation for proper test planning and documentation with the following checklist:
A standard QA is not enough for software testing in healthcare; it requires much more, whether it be regulatory alignment, precision, or patient-first thinking. It also requires a proper validation of each layer, right from data security to device heterogeneity and EHR integration.
Moon Technolabs offers world-class software testing services in healthcare, backed by in-depth domain expertise and compliance-based strategies. Stay in touch with us for an expert-led IoT testing assessment and tailored solutions.
01
02
03
04
Submitting the form below will ensure a prompt response from us.