Table of Content
Blog Summary:
This guide presents a detailed comparison between private and public blockchains to help you understand the right option for your organization. We have explained their advantages, use cases, major differences, etc. Start reading the entire post now.
Table of Content
According to MarketsandMarkets, the worldwide Blockchain market size is likely to grow to $248.9 billion by 2029, up from $20.1 billion last year (2024). The stats reflect the growing demand for Blockchain among businesses for various reasons, such as transparency, security, and efficiency.
Businesses have two options for using blockchain: private and public blockchains. So, which is the right option to go with? It’s indeed a crucial decision that businesses need to make. They need to make a detailed comparison of private Blockchain vs. public Blockchain, which helps them shortlist the best option for their businesses.
In this post, we will help you make the best decision by letting you select the right option between these two Blockchains. Let’s explore.
A private blockchain is a decentralized ledger that works with a closed network. Only an authorized participant can access it, unlike public Blockchain, which is accessible to anyone. An individual organization controls a private Blockchain.
They provide improved security, privacy, and efficiency and are a perfect choice for many enterprises and businesses that handle sensitive data. It ensures fast and more scaled transactions, mainly due to limited participants, and is also controlled through consensus mechanisms.
Be it supply chain, finance, healthcare, or others, many industries leverage Blockchain for highly secured record keeping, process automation, smart contracts, and more. Private Blockchain offers more control and regulatory compliance.
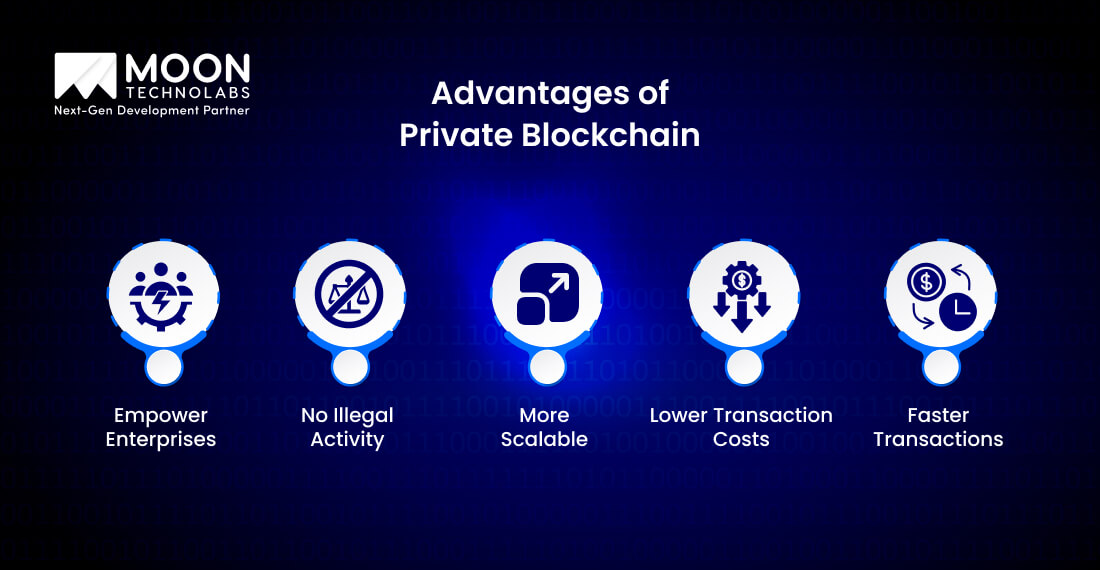
Private Blockchain brings a plethora of advantages to businesses and enterprises. We will take a detailed overview of each advantage. Let’s explore them in-depth;
With a private Blockchain, one can get full control over their data and transactions. Businesses find it convenient to customize the network to match their specific requirements, including data privacy, regulatory compliance, governance, and more. A private blockchain is useful when it comes to minimizing any unauthorized modifications or risks.
Public Blockchain often raises major concerns about potential misuse or illegal activities like fraudulent transactions, money laundering, etc. Private Blockchain minimizes the chance of working under a closed network.
It requires a strict access control mechanism or identity verification to ensure that only authorized users engage in transactions. This ensures the system’s high security and transparency.
Scalability is a crucial factor for businesses that need to process a larger volume of transactions. Private blockchains are quite scalable compared to public Blockchains. They work within a highly controlled environment with only a couple of participants.
It minimizes network congestion while letting businesses process multiple transactions more efficiently. Enterprises can optimize network performance by customizing consensus mechanisms to boost transaction scalability and speed.
Public Blockchains often need miners to validate transactions, which leads to increased transaction fees. Private Blockchains minimize the necessity for mining and also depend on a consensus model among many authorized participants.
It minimizes transaction costs, making it cost-efficient for organizations. Businesses can also ignore expensive intermediaries, resulting in further savings.
Speed is an important factor in Blockchain applications, especially for many industries such as supply chain, finance, and more. Private Blockchains provide quick transaction processing since they don’t rely on a vast network of anonymous nodes.
With fewer participants and highly efficient consensus mechanisms, transactions are completed in less time rather than hours and minutes. It makes private Blockchain a perfect choice for businesses that need real-time processing and fast settlements.
Private blockchains can restrict access to unauthorized participants, which makes it perfect for many sectors that need control and privacy. Let’s understand several use cases.
With private Blockchain, organizations can track products in real time, from production to delivery, enhancing supply chain transparency.
Many businesses can easily verify products while ensuring authenticity, minimizing fraud, streamlining operations, etc. Smart contracts automate transactions easily, offer on-time payments, and also ensure full compliance on a daily basis.
Private Blockchains can securely store and manage patient data. Hospitals, insurers, and pharmaceutical companies share medical records with several authorized entities.
Blockchain reduces administrative costs and thus improves patient care. It plays a vital role in drug traceability and prevents counterfeit medicines from entering the supply chain.
Private Blockchain has also significantly impacted banking by offering quick and highly secure transactions. Many banks use private blockchains for various processes, such as loan processing, cross-border payments, fraud prevention, and more.
Smart contracts ensure automated settlements, which minimize operational costs and thus increase efficiency. Blockchain also improves know-your-customer (KYC) compliance by offering a secure and immutable customer identity verification process.
Private Blockchain effectively boosts financial services like asset management, insurance, trading, and more. Insurers leverage Blockchain to minimize fraud, automate claims processing, speed up payouts, and more.
Asset managers use Blockchain to tamper-proof and transparently record investments. Blockchain provides full authenticity and security of transactions, reducing risks and maximizing regulatory compliance.
As mentioned, the public Blockchain is an open network, and anyone can access it. An individual doesn’t need permission to access it. This Blockchain functions on a distributed ledger technology where transactions are verified easily with the help of proof of stake (PoS), proof of work (PoW), and more.
Whether it’s immutability, security, or transparency, public Blockchain offers several advantages. That’s why it’s considered the top choice for cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum and Bitcoin.
Meanwhile, the major issues that public Blockchain faces are energy consumption and scalability. Their global accessibility and trustless nature make them a perfect foundation for decentralized apps and smart contracts.

Public Blockchain also brings numerous advantages, such as transparency, decentralization, and a secure network. Let’s explore certain key advantages.
The major benefit of public blockchains is that they are open to anyone with an internet connection, ensuring their higher accessibility.
Whether you are a businessman or an individual, you can participate in public Blockchain without any restriction. It ensures financial empowerment, especially in areas with limited banking access.
Public Blockchain leverages cryptographic techniques and decentralized consensus mechanisms, including PoS and PoW, to secure every transaction. Since the network is distributed across different nodes, data altering or hacking becomes impossible, making sensitive transactions tamper-proof.
A Public Blockchain records each transaction in an immutable ledger that is visible to every participant. This level of transparency improves trust among users and effectively minimizes corruption and fraud.
Governments and businesses can use this feature to build credibility and accountability in supply chains, financial operations, and governance.
Another advantage of public Blockchain is that it offers an open-source environment, which allows developers to build smart contracts and decentralized apps. This promotes continuous innovation across many industries, such as healthcare, finance, and real estate.
In addition, the decentralized nature allows new business models to remove intermediaries, boost efficiency, and minimize costs.
Anyone can participate and contribute to the public blockchain, be it a developer, user, or miner. This is good for decentralization and collaboration, which ensures that no single entity controls the network. It also improves network resilience, making systems more powerful against attacks or failures.
Public Blockchain is used for various purposes, whether for government or private use. We will discuss some of the popular use cases of public blockchains here.
Public Blockchain plays a vital role in improving electoral integrity. It assures immutability, transparency, and security even during the voting process. Blockchain-based voting systems are useful for preventing fraud and offering complete, verifiable results.
It ensures a tamper-proof and remote election. Both Governments and businesses leverage Blockchain for governance decisions, making the entire process fully accountable and democratic.
Another popular use case of public Blockchain is cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum and Bitcoin. These digital currencies ensure borderless transactions even without any intermediaries, which minimizes cost and thus increases financial inclusion.
Smart contracts automate further processes, including insurance, lending, decentralized finance, etc. They offer secure and efficient alternatives to traditional banking.
Public Blockchain has also greatly impacted the creative industry by allowing musicians, artists, writers, and others to take direct ownership of their work.
Besides, Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) allow creators to tokenize several digital assets while ensuring authenticity. They also enable direct monetization without any intermediaries and help artists gain full control over royalties and intellectual property rights.
Blockchain ensures peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading. It allows individuals to purchase and sell surplus renewable energy without depending on centralized utility companies.
Smart contracts even facilitate automated transactions while ensuring fair pricing and transparency in energy distribution. This decentralized approach ensures sustainability and efficient energy management.
Both private and public Blockchains serve various purposes, use cases, etc. We will examine in detail some major differences between these two important types of Blockchain based on their transparency, access, control, decentralization, and accessibility.
As mentioned, a public Blockchain allows anyone to access and participate in it. Any organization or individual can participate, read, and validate their transactions. For instance, Ethereum and Viotcoi are the most popular examples of public networks.
On the other hand, a private Blockchain is limited only to a specific group of participants. Only authorized personnel can access it and interact with the network. That’s why it’s considered an apt choice for enterprises and organizations that need confidentiality.
Private blockchains and public blockchains differ in terms of the level of transparency they offer.
Public blockchains offer a high level of transparency and ensure that every transaction is visible to each participant on the network. This ensures both security and trust since no single entity can manipulate data without being checked.
On the other hand, private transparency offers limited transparency as only authorized persons can check the transaction history. Many businesses leverage private Blockchains to keep sensitive data confidential while utilizing the security features of Blockchain.
Decentralization is another important feature of Blockchain, but it also varies depending on the type of Blockchain. Public Blockchain is fully decentralized since control is distributed among different participants. No single authority has ownership, which ensures a high level of security and trust.
Private Blockchain is centralized or even partially decentralized since it allows only a specific group of participants to gain complete control over the network. It ensures fast transactions but also tends to raise huge concerns about data manipulation.
The level of control over the network signifies who gets the authority for changes. In a public Blockchain, no individual entity gets control of the Blockchain. Consensus mechanisms ensure that every participant validates transactions fairly.
Specific organizations manage private Blockchains. They are responsible for everything, including rules, updates, and permissions. This gives businesses greater control over their operations but also limits the openness of networks.
Another major difference between private and public blockchains is the ease of use and joining of the Blockchain network. Public Blockchain is available for anyone with a fast internet connection, which is why it is the right choice for many decentralized apps and open-source apps.
On the other hand, private Blockchain requires special permission to join, which makes it a good choice for many industries, such as healthcare, banking, and supply chain management, where data security is highly important.
With public Blockchain, users can participate in transactions anonymously using cryptographic addresses rather than real-world identities. This makes public Blockchain a perfect choice for financial transactions where privacy is necessary.
Private Blockchains require participants to verify. They don’t include any provision of anonymity since access is fully restricted to authorized users. Organizations and enterprises focus on private Blockchains to maintain full control over participants and comply with various regulatory requirements.
In public blockchains, security is maintained through many cryptographic techniques and various consensus mechanisms. Its decentralized nature makes it fully resistant to censorship and various hacking attempts. For example, altering data requires consensus from a number of nodes.
A Private Blockchain has various nodes and is controlled through individual organizations. While it makes transactions more efficient and faster, it also creates a single point of failure. Meanwhile, access to overall control mechanisms and permissions can boost security by limiting many unauthorized activities.
Public Blockchain consumes a vast amount of energy due to the necessity of extensive computational power for validation transactions. This higher energy consumption has increased concerns about sustainability.
Private Blockchain uses various alternative consensus mechanisms, such as proof of authority (PoA) or practical byzantine fault tolerance (PBFT). These mechanisms consume less energy, and transactions are processed with a limited number of trusted nodes while minimizing the computational workload.
The most popular examples of public Blockchains include Ethereum, Bitcoin, Solana, and more. As an open-source network, it enables anyone to join and participate in mining and verifying transactions.
The most popular examples of private blockchains include Corda, Fabric, Quorum, and others. These Blockchains are used mainly for enterprises for apps such as financial transactions, supply chain management, identity verification, and more.
Transparency is another important feature of any public Blockchain. Every transaction data is recorded and accessible to anyone, including the ledger. Though transactions are anonymous, they remain visible to every participant as well.
In private blockchains, data visibility is limited mainly to authorized participants. Organizations have full liberty to control who has access to any specific information. This is perfect for businesses that handle sensitive data and is also necessary to comply with privacy regulations.
Whether you should opt for a private Blockchain or a public Blockchain depends entirely on your business needs. If you seek a private Blockchain that offers higher efficiency and is full of control, you should choose private Blockchains.
Besides, when you look for decentralization and transparency, you should always opt for public Blockchains. So, the final decision entirely depends on scalability, security, governance needs, and more.
The future of Blockchain technology reflects the transformative growth across many industries. With advancements in interoperability, scalability, sustainability, etc., blockchain is set to become more efficient and widespread in adoption.
Apart from innovations such as sharding, Layer 2 solutions and zero-knowledge proofs will improve transaction speed and privacy. Whether it’s NFTs, DeFi, or enterprise Blockchain apps, they tend to continue expanding.
Governments integrate Blockchain for secure transactions and digital identities. With the emergence of quantum computing, cryptographic security tends to emerge. With continuously increasing mainstream adoption and regulation, the future of Blockchain promises a decentralized, transparent, and secure digital economy.
At Moon Technolabs, we work as a reliable partner for development and implementation. It provides more advanced and tailored business solutions. We have a proven track record in AI, software development, automation, cloud solutions, and more.
With us, you can be assured of higher scalability, smooth integration, efficiency, and more. Our team of consultants and skilled developers follows a fully agile approach and delivers fully customized solutions that align perfectly with your business objectives.
Our experts focus on security, innovation, performance, and more while ensuring long-term success. From small companies to enterprises, we assist businesses with powerful digital transformation strategies, exceptional support, cost-efficient solutions, and more. We deliver future-ready solutions to help you gain a competitive edge in your industry.
Unsure whether to choose a private or public blockchain? Our experts can help you select the best blockchain solution tailored to your needs.
Private and public blockchains have distinct benefits tailored to different requirements. You may have already decided on the right option between these two options. Well, the choice between these two relies heavily on the goals and use cases of businesses.
At Moon Technolabs, we play an important role in Blockchain development. Our team provides complete expert guidance and tailored solutions to assist businesses in implementing the best Blockchain technology for innovation and efficiency.
01
02
03
04
Submitting the form below will ensure a prompt response from us.