Table of Content
Blog Summary:
This blog compares NativeScript and React Native for cross-platform app development, highlighting their performance, UI control, scalability, and suitability for business-specific use cases. It guides businesses in choosing the right framework based on real-time data needs, app size, connectivity, and developer expertise, helping ensure faster, scalable, and cost-effective mobile app delivery.
Table of Content
Businesses that don’t invest in high-performing mobile apps risk being left behind.
However, building native apps for both platforms can be expensive, time-consuming, and technically fragmented. This is why cross-platform frameworks, such as NativeScript vs React Native, are rapidly gaining popularity among developers building enterprise-grade applications.
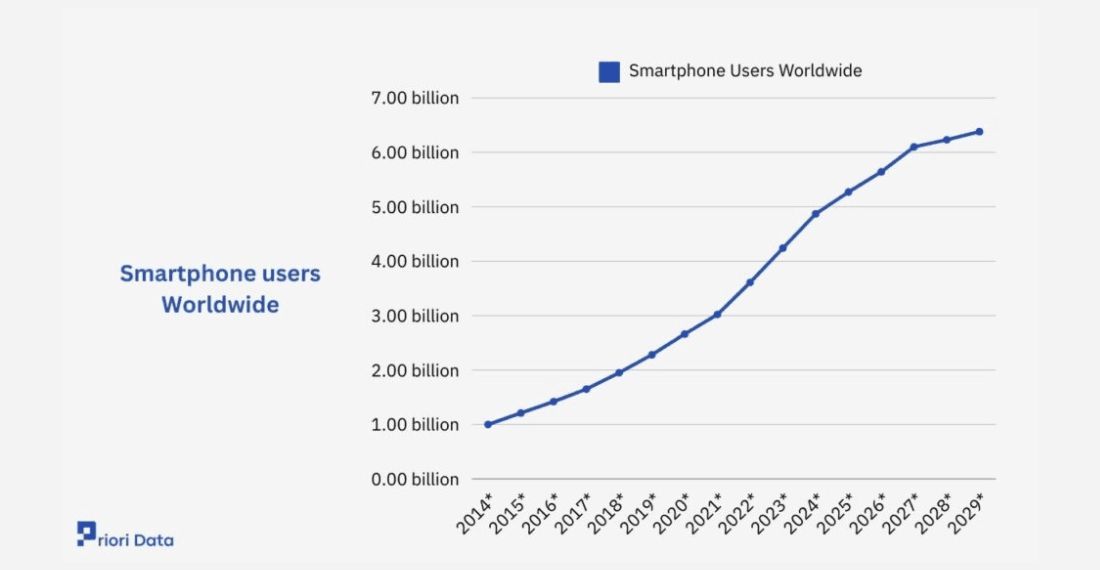
Today, there are approx 4.9 billion smartphone users worldwide, out of which 70% are using Android snmartphones. In fact, Research and Markets predicts that the smartphone market is expected to reach 6.38 billion by 2028.
React Native, backed by Meta, powers global apps like Facebook, Instagram, and Bloomberg. Its counterpart, Native Script, offers direct access to native APIs, supporting both Angular and Vue.
But which one should your business choose?
This blog goes beyond surface-level comparisons and delves into real-world app examples, performance benchmarks, and development needs, helping you make a confident and informed choice.
Native Script provides direct control over an app’s native features without requiring any bridging code, by injecting them directly into the JavaScript virtual machine. It focuses on creating fully native apps using JavaScript and CSS, which has contributed to making it one of the leading platforms for iOS app development and Android app development.
It features a personalized tech stack that enables developers to build both cross-platform and native apps, prioritizing performance when it matters, resulting in fluid and responsive apps.
It also provides developers with enough flexibility to share a single codebase across both Android and iOS apps. This helps them reduce development time and maintenance costs by offering direct access to native APIs.
Here are some advantages of considering NativeScript based on different instances of app development:
When you need tight integration and access to native APIs without waiting for third-party plugin support, NativeScript offers a better choice, as it provides easier integration with libraries and native SDKs.
When you need to develop an app that requires real-time interaction without any lag between UI actions, NativeScript compiles the UI easily into platform widgets. Hence, developers can use platform-specific optimizations.
For developing apps that require native UI elements, such as segmented controls and secure input fields, NativeScript allows developers to render actual UI components, including UIButton and UITabBar. This helps in loading conditional UI per platform, creating consistent designs.
For developing apps that need similar features to Angular-based apps, Native Script + Angular allows you to reuse services and business logic from existing web apps. It provides support for Angular CLI, modules, and Ivy rendering, improving feature parity and reducing team costs.
Building apps such as a startup’s MVP requires rapid development cycles and often needs frequent UI/UX changes. In such cases, Native Script provides support for HMR, enabling developers to edit CSS, TypeScript, or XML and see live changes without needing to reload.
React Native is a JavaScript framework introduced by Facebook in 2015. While they initially introduced it as only an iOS version, they introduced the Android version in September because the iOS version turned out to be a huge success.
React Native app development leverages the capabilities of both JavaScript and React, empowering developers to create native apps for both iOS and Android.
Due to this, it’s easier to share a single codebase across different types of contributors, thereby enhancing productivity. It helps build high-performing native apps by leveraging device features such as GPS and the camera.
React Native is compatible with all the latest OS versions, allowing developers to build feature-rich applications. It also has a smoother learning curve for the developers who are already familiar with JavaScript.
With easy access to an extensive database of third-party libraries, development tasks are more streamlined.
Here are some advantages of considering React Native based on different instances of app development:
For developing cross-platform and native apps that need to scale across multiple platforms, from Android smartphones to Mac desktops, developers require audio and video capabilities, as well as chat SDKs. React Native is your ideal solution because it has a large ecosystem of ready-made SDKs, such as Agora and Sendbird.
To learn more about building scalable apps for iOS and beyond, check out our comprehensive iOS App Development Guide.
When you need to build highly interactive dashboards that need integration with CI/CD and component modularity, React Native is the best bet as it leverages declarative syntax and component-based UI. Together, all these components make app state management easier for the developers, providing tools like Redux, Mobx, and Recoil.
React Native is a highly strategic language, making it ideal for apps that require real-time integration with dynamic APIs. Offering access to thousands of community-built libraries and SDKs such as Lottie, Firebase, and Stripe, it’s a go-to framework for building fast and modern apps.
The code reusability feature of React Native allows developers to write code once and deploy it on any platform. This reduces infrastructure costs by allowing a single team of developers to save efforts on engineering while also extending the functionality. Its high compatibility with third-party features also helps reduce the need for a custom build.
For developing apps with modern animations for user engagement, high iteration speed is required due to dynamic user preferences and rapid updates. React Native is the preferred choice, as it provides built-in libraries such as react-native-reanimated and react-native-gesture-handler.
Let us help you guide your decisions by evaluating your app complexity, budget, and timelines.
Both NativeScript and React Native offer robust solutions for businesses seeking to develop mobile applications. However, the right choice depends on the type of app you want to develop and your development goals. Ultimately, this decision extends beyond selecting a stack that addresses your specific business needs.
Let’s understand these differences in detail:
Native Script provides true native API access without requiring the writing of bridges or the use of third-party wrappers, making it easier to access native functionality and reducing the likelihood of errors.
React Native delivers smooth performance through native rendering and supports optimizations via the Hermes engine. While ideal for most business apps, it relies on a JavaScript bridge, which can introduce latency during frequent native interactions, especially in animation-heavy or real-time apps with high-performance demands.
Native Script offers robust support for both existing and new libraries, utilizing its command-line interface (CLI) to enhance developer productivity. It is faster to implement and maintain, without requiring any existing plugins, and supports Angular and Vue as first-class citizens.
React Native boosts development speed due to its hot reloading feature. It reduces duplication and speeds up iteration cycles, further streamlining testing and debugging.
Since the UI of Native Script is built using XML markup and supports CSS styling, it closely resembles web app structures. XML-based UI layouts, combined with CSS styling, are a great combination for building applications with heavy form-based layouts and dashboards that require input-heavy functionality.
With a rich and customizable UI, React Native is highly adaptable for developers to work with and style its components. Using JavaScript and CSS-like Syntax, its declarative UI helps simplify building user interfaces that are consistent across platforms.
Native Script contains a marketplace for all its official plugins, curated for developers to access native device features for reliability. It reduces onboarding while leveraging existing skills, helping minimize project ramp-up times and costs.
With Native Script, you can easily remove unnecessary and unused UI components and plugins using Angular CLI and Vue build tools.
As one of the largest and most active developer communities, React Native offers extensive documentation, open-source libraries, and GitHub contributions to help developers resolve any issues they may encounter.
Native Script provides developers a great opportunity to work with different app versions. They can update their features while also getting access to seamless support for third-party plugins and libraries.
React Native’s Hot Reloading capability enables developers to accelerate their mobile app development process, allowing them to see changes in real-time without needing to restart the app.
NativeScript apps tend to have larger app sizes compared to those built with lightweight frameworks due to bundled native components and plugins. However, developers can remove unused features or UI elements using Angular or Vue build tools.
React Native apps generally have moderate app sizes, which are even larger than fully native apps since they include a JavaScript runtime. However, it also offers tools such as Hermes and ProGuard to reduce app size, resulting in better performance.
NativeScript apps can implement native-level security protocols, such as biometric authentication, secure storage, and encrypted communication. These are ideal for healthcare or finance apps that require compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI DSS standards.
React Native adheres to JavaScript best practices to enhance basic app security; however, it may require more advanced measures for apps with higher risks. Developers can integrate native modules for encrypting data and authentication processes.
NativeScript supports unit testing, end-to-end testing, and UI testing through tools such as Karma, Jasmine, and the NativeScript testing framework. With Angular or Vue integration, teams can adopt familiar testing patterns, though debugging may be more complex.
React Native’s browser-based environments provide support for the full testing stack. It includes Jest for unit testing and React Native testing library for integration testing. With Detox and Appium for end-to-end testing, developers can accelerate the testing and debugging cycles.
In Native Script, developers can access their reusable components to create modular apps that are also easier to scale according to requirements. They can either utilize these components in various parts and areas of a project or apply them to a new project.
React Native offers developers a bridge architecture that helps connect JavaScript with native app components, enabling cross-platform development. However, it may create latency in apps where performance is critical. Fabric Renderer and TurboModules are two tools that enhance rendering speed and reduce memory usage.
With a solid understanding of XML, along with JavaScript and CSS, developers can build efficient and accessible application development processes using NativeScript. It also renders native UI components directly, which gives better control over native compliance.
While allowing developers to build cross-platform apps with a single codebase, React Native offers consistent performance levels for iOS and Android. Creating native-like experiences for apps, it also offers React Native web to provide extended support for browsers.
Based on the above comparisons between Native Script and React Native, it is evident that they share many similarities, yet differ in several key features. For businesses with specific development needs, these differences become very apparent and meaningful.
Let’s explore the practical differences that would lead a business to choose one over the other based on real-world development issues:
| Factors | Choose Native Script | Choose React Native |
|---|---|---|
| Native capabilities | Your app requires deep or frequent use of native device capabilities. | You rely mostly on community packages for native features |
| Implementation and maintenance | Your app requires faster implementation and maintenance, especially when no plugin is available. | You want your app to have modular architecture, dashboard-friendly libraries, and integration support. |
| Team development efforts | Your teams want to reduce onboarding, ramp-up time, costs, and leverage existing skills. | You want to invest in rapid cross-platform deployment and easy hiring across time zones. |
| Design and UI | Your app design/UI workflow is tightly coupled with web-like styling and logic separation. | Your app requires accelerated UI development for better engagement through improved animations and rapid iteration. |
| Real-time data | Your app requires real-time data capture, native camera filters, or high-frequency hardware events. | You want to offer instant data refreshes without glitches with reduced backend API development overheads. |
| Market and app size | Your app is designed for emerging markets with limited storage capacity. | You want to develop smaller-sized apps that are easy to scale in multiple markets and improve retention. |
| Connectivity and downloads | Your app is designed for regions with poor connectivity, and you want faster app downloads. | You want to develop apps that work smoothly even in unreliable networks and allow download-heavy workflows in the background. |
Let our experience across industries help you simplify your tech stack decisions that align with your app vision.
Choosing between React Native and NativeScript is a strategic decision that can have a direct impact on your app’s performance, scalability, and development speed.
On the one hand, NativeScript provides unparalleled native API access, making it ideal for building highly customized user interfaces, enterprise dashboards, and input-heavy forms.
In contrast, React Native app development offers unmatched developer flexibility and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for apps that rely on real-time data for emerging markets.
So, what kind of app is your business building?
At Moon Technolabs, we specialize in solving these dilemmas related to custom app development services. Our team of expert developers helps you evaluate such trade-offs, optimize tech choices, and build cross-platform apps that are not only functional but also future-ready.
Let’s build what your users truly need. Contact our experts today.
01
02
03
04
05
Submitting the form below will ensure a prompt response from us.