Table of Content
Blog Summary:
Explore the differences between chatbots and AI assistants, their unique roles in customer engagement, and how businesses can leverage them for better service, efficiency, and automation in the age of conversational AI.
Table of Content
Businesses worldwide are transitioning from basic chatbots to AI-powered assistants that can reason, remember, and take action. But what’s the real difference between an AI chatbot and an AI assistant, and does it really matter to your bottom line?
For small and large businesses that are under constant pressure to do more with less, the difference between the two could be worth hundreds or thousands of dollars. Switching to AI assistants can transform their support economics by unlocking new levels of productivity.
Fortune Business Insights predicts that the combined value of chatbots and AI assistants is expected to reach USD 61.69 billion by 2032, growing from USD 14.79 billion in 2025. Hence, the most pivotal question facing businesses today is: Are their current chatbots evolving fast enough to keep up with customer demand?
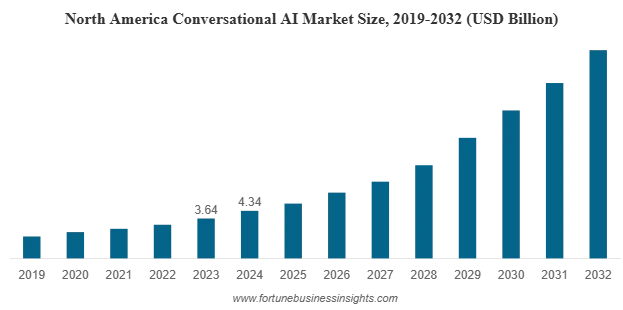
In the sections that follow, we’ll dive deeper into the debate over chatbots vs. AI assistants and explore the transition from traditional chatbots to intelligent AI assistants.
Chatbots serve as the functional backbone of many businesses seeking to expand their digital customer base and increase engagement. For customer experience (CX) leaders, IT and product teams, and SMB owners, chatbots are the key to ensuring that services run smoothly.
Even as conversational AI assistants evolve, most customer interactions still involve routine tasks. Chatbots serve as the primary point of contact for handling simple requests and forwarding all complex queries to human staff.
Whether it’s 2 in the afternoon or the morning, customers can easily reach out to the brand support and get answers to their basic questions from chatbots. It doesn’t matter if your live support team is asleep, chatbots are always available and ready to answer customer queries, help them file a complaint, and even provide live order updates.
It is crucial to note that most customer complaints regarding delays are not due to the limitations of chatbots. They arise because the workflows of bots are not properly designed, and they also lack proper integrations. Upgrading and redesigning chatbot workflows and services can address these issues and even help generate a higher ROI.
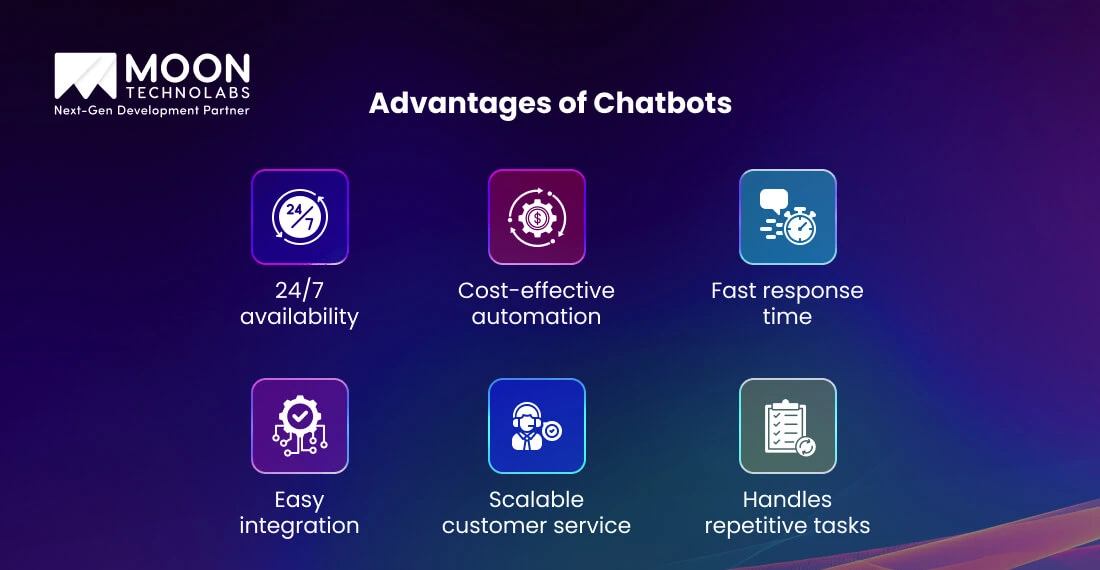
The following are some data-backed wins with the most fundamental benefits, demonstrating that chatbots aren’t just “nice to have.” They unlock measurable savings, revenue gains, and enhanced customer experiences across industries, making them a big reason why they remain essential:
Chatbots enable your users to interact with your brand at any time by resolving simple queries and reducing support wait times by 30%. At a fraction of the cost, chatbots are found to resolve routine queries for up to USD 0.70 per interaction, compared to USD 6–14 with live agents.
Chatbots can efficiently manage a large volume of repetitive administrative tasks, such as order lookups, password resets, and basic FAQs. Amtrak introduced its bot Julie, which helps the brand increase online bookings by 25% and save $1 million in service costs.
Bank of America’s chatbot, Erica, is capable of handling 2 million client interactions daily, with 60% of them providing proactive insights. It saves 10 million staff hours by providing faster and smarter self-service based on structured data, and minimizes errors that occur from manual responses.
Chatbots are easily scalable when required to handle sudden surges in user inquiries related to product launches. Such virtual assistants don’t require any increase in headcount, translating to a dramatically lower cost of serving. Telecom and retail deployments report up to 70% lower cost-per-chat and first-contact automation of 60-80% of FAQs.
Chatbots also give instant responses and can simultaneously serve thousands of users, cutting live queue times. Kia’s Facebook Messenger bot, “Kian,” helps the brand achieve three times more conversions than its website and generates 50 times more engagement.
The upgrade from static and basic bots, which are scripted and rule-based, to developing autonomous AI agents requires a modernized tech stack. Since today’s customers don’t want to play by the rules and don’t depend on rule-based, simple, and scripted interactions, businesses need to rethink their automation strategies.
The Forbes market data show that out of 86% of consumers who have already interacted with chatbots, at least 60% think that AI assistants can enhance their experience through intelligent and personalized interactions.
This gap highlights the potential for businesses to upgrade their basic bots to AI assistants capable of understanding intent, retaining context, and autonomously resolving complex queries.
Businesses today face tremendous pressure to reduce costs, accelerate decision-making, and deliver exceptional customer and employee experiences. They have to juggle vast data volumes, complex workflows, and high customer expectations.
While chatbots lay the groundwork for 24/7 automated interactions, AI assistants elevate automation from simple rule-based exchanges to context-aware and action-oriented support.
AI assistants address these imperatives by:
Empower your business with chatbots that deliver instant responses around the clock, reduce wait times, and automate routine tasks at lower operational costs.
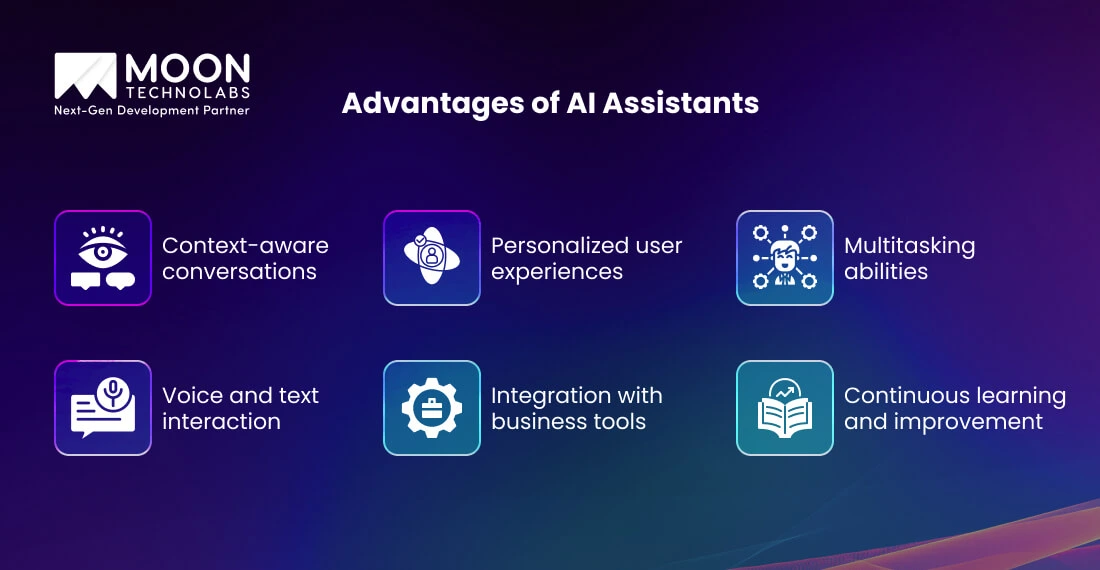
By combining NLP, machine learning, and enterprise integrations, AI assistants act as “digital co-pilots”. They are instrumental in accelerating everyday tasks, surfacing critical insights, and fostering measurable ROI across functions.
Rather than just presenting raw data, AI assistants analyze information across multiple sources to provide actionable and contextual recommendations in natural language. In financial services and healthcare, this translates to 61% faster decision cycles and up to 85% greater efficiency in processes.
AI assistants leverage historic data, real-time signals, and advanced recommendation engines to drive sales directly. For retailers and e-commerce brands, they boost personalized suggestions, resolve abandonment issues, and accelerate sales cycles. H&M’s AI shop assistant boosted conversion rates by 25% and incremental revenue by 30%.
By handling repetitive process steps, AI assistants make entire departments more agile and reduce burnout. Software engineers leverage “AI code assistants” that automate code reviews and suggest fixes. HR and operations teams utilize AI to address internal queries, update records, and facilitate compliance.
AI assistants deliver better support interactions and engagement for large enterprises, automate data collection, facilitate appointment scheduling, and streamline claim processing. Deploying AI-driven route optimization and shipment tracking yields a 3x ROI, freeing up staff for strategic work.
AI assistants continuously learn and adapt based on new data, feedback, and evolving business requirements. They enable effortless scaling across products, languages, and regions while also offering robust fallback or escalation strategies for unhandled requests.
As businesses accelerate their digital transformation, understanding the practical differences between chatbots and AI assistants is crucial. Both serve as digital frontlines for customer service and operations, yet their capabilities sharply diverge.
Here’s a tabular comparison between both:
| Feature | Chatbots | AI Assistants |
|---|---|---|
| Level of Complexity | Basic, rule-based responses | Advanced, context-driven reasoning |
| Context Handling | Limited to a session or single interaction | Maintains context across sessions, users, and channels |
| Personalization Capabilities | Minimal; mostly generic | High; adapts replies based on user data and behavior |
| Learning Ability | Manual updating of scripts only | Learns from interactions; self-improving via ML |
| Task Execution Scope | Handles predefined, simple tasks | Executes complex, multi-step workflows |
| Interaction Channels | Typically, web or messaging only | Omnichannel: web, app, voice, email, IoT, etc. |
| Integration Capabilities | Limited, basic data sources/APIs | Deep integration with CRMs, ERPs, databases, and SaaS |
| User Experience | Predictable but static; low empathy | Dynamic, human-like, adaptive, and more natural |
While chatbots and AI assistants both aim to automate and enhance digital interactions, their underlying technologies, investment requirements, and operational impact diverge.
Below, we compare the two across key technical and practical dimensions, diving deep into the technical and business trade-offs for organizations evaluating a conversational solution.
Chatbots usually rely on decision trees, keyword detection, and rules-based frameworks (e.g., Dialogflow, ManyChat). AI Assistants use advanced NLP, ML, and deep learning frameworks (e.g., OpenAI GPT, Rasa, IBM Watson).
Customization with chatbots often requires manually updating scripts, which have limited capability for natural-language understanding. They are also less expensive to build and deploy.
AI assistants can be integrated with enterprise APIs, databases, and cloud platforms for richer, more dynamic interactions. They also demand greater upfront investment for development, integration, and custom model training.
Chatbots can often be launched in days or weeks with off-the-shelf tools or templated flows. Their costs are mainly tied to the development of simple scripts and initial integration.
AI assistants require a longer runway, typically ranging in months for data integration, model training, and organizational alignment.
Chatbots are ideal for tasks that are narrow and predictable, such as FAQs, order tracking, and appointment booking.
AI assistants learn and adapt to complex patterns from existing operations. They often have evolved workflows such as customer onboarding, technical troubleshooting, or sales enablement.
Chatbots scale linearly where new use cases require new flows or scripts, adding to maintenance overhead.
AI assistants scale exponentially, often requiring them to handle surges in complexity or volume through self-learning and cross-departmental integration.
The evolution from basic chatbots to sophisticated AI assistants brings both transformative benefits and a new set of complex challenges. Below is a detailed examination of the challenges organizations encounter when implementing, scaling, and sustaining these technologies:
Traditional chatbots only retain context within a single session and handle one intent per interaction, forgetting previous conversations. This frustrates users who are looking for multi-layered questions or scenarios involving multiple workflows.
When users raise queries with novel phrases and requests, bots often fail to route or resolve issues, instead defaulting to generic responses. Since predefined scripts with brittle flows drive chatbots, updating them with new intent as per changes in processes leads to errors and “spaghetti logic.”
Chatbots lack advanced NLU, leading to poor comprehension of nuanced language. Without user memory or access to data, bots often provide generic responses, which can miss opportunities for personalized support.
Chatbots often misunderstand slang, emotions, or unexpected input, resulting in a reported error rate of 20–25% in complex queries. Simple chatbots may not connect to core CRM, ERP, or knowledge base systems, limiting their ability to take meaningful action.
Requiring separate deployments for web, mobile, and social channels adds complexity to managing consistent behavior and reporting across platforms. It leads to more complex scripting since user needs are diversified, which makes scaling to handle large volumes and new markets resource-intensive.
AI assistants pose real operational, technical, and cultural challenges. Resolving these barriers is crucial for businesses seeking to automate at scale, protect sensitive data, and provide truly exceptional digital experiences for customers and teams.
AI assistants require ongoing updates to reflect product changes, new regulations, and evolving language. This maintenance can be expensive without robust MLOps to facilitate a full enterprise rollout, while exposing unforeseen edge cases and integration issues.
Business data is often siloed, outdated, or incomplete, which often results in AI assistants making flawed recommendations or providing inaccurate responses. Mishandling data can lead to both legal trouble and erosion of trust.
AI assistants rely on accurate, comprehensive information to generate reliable outputs. Successful deployment requires seamless integration with CRM systems, databases, and third-party applications. APIs may be inconsistent or unavailable, and mapping data securely across systems increases setup time and cost.
Many AI assistants operate opaquely across large datasets, making it difficult for users and auditors to understand how decisions are made. For regulated industries, AI outputs must be explainable on demand, which makes it challenging to work with large language models.
Employees may see AI as a threat to job security or feel frustrated with initial integrations, leading to lower adoption rates and ROIs. When faced with limitations or errors, disappointment can lead to disengagement.
Step beyond basic automation and deliver personalized, context-aware experiences by deploying smart AI assistants that understand and act on complex queries.
Businesses should view chatbots as an entry point for automation and AI assistants as the strategic evolution that unlocks deeper efficiencies and revenue opportunities. To move forward, it’s essential to assess use cases and scenarios to identify repetitive tasks and decision workflows ripe for AI augmentation.
Here’s an overview of when to choose which option:
| Scenario | Recommended Solution | Why Is It The Right Option? |
|---|---|---|
| Simple FAQ & Order Status | Chatbot | Low implementation cost; handles up to 80% of straightforward queries with scripted flows. |
| 24/7 Personalized Customer Support | AI Assistant | Context-aware responses, personalization engines, and the ability to route complex issues. |
| Data-Driven Sales Recommendations | AI Assistant | Leverages customer data to generate upsell/cross-sell suggestions in real time. |
| Developer Productivity & Code Reviews | AI Code Assistant (a subset of AI Assistant) | Automates pull request feedback and generates code snippets, boosting developer efficiency. |
| Proactive Workflow Automation (e.g., logistics) | AI Assistant | Autonomous decision-making for routing, anomaly detection, and end-to-end orchestration. |
Rule-based chatbots alleviate workloads and handle urgent customer queries; however, as customer needs become more complex, upgrading to next-generation AI assistants becomes essential. Is your business ready to accelerate its transformation by automating routine tasks?
We can help you transform your existing chatbots with AI development services designed to cut wait times, deliver consistent support, and boost customer satisfaction. Upgrade your business to keep up with the high-volume sectors by partnering with Moon Technolabs:
Our AI developers specialize in building both robust chatbots and advanced AI assistants. We have developed AI solutions for leading global clients who have reported significant gains in cost efficiency, satisfaction scores, and team productivity.
Get in touch with our AI experts TODAY to book a call.
01
02
03
04
Submitting the form below will ensure a prompt response from us.